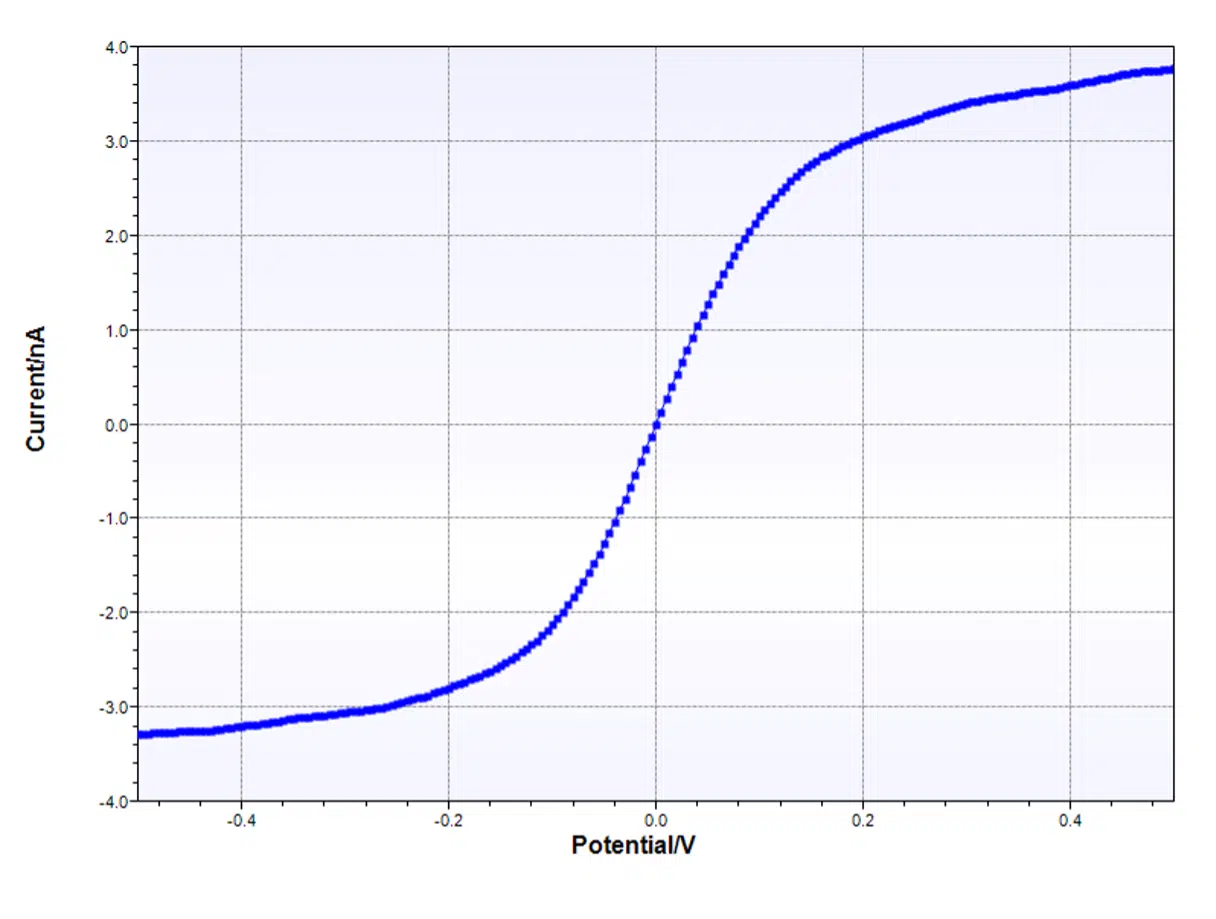
Normal Pulse Voltammetry (NPV)
Normal Pulse Voltammetry (NPV) is an electrochemical technique. With Normal Pulse Voltammetry the influence of diffusion limitation on your I-E curve (Cottrel behavior) is removed.
In Normal Pulse Voltammetry (NPV) a potential scan is made by making constantly larger potential steps of pulse. NPV is normally more sensitive than LSV, since the diffusion layer thickness will be smaller, resulting in a higher faradaic current.
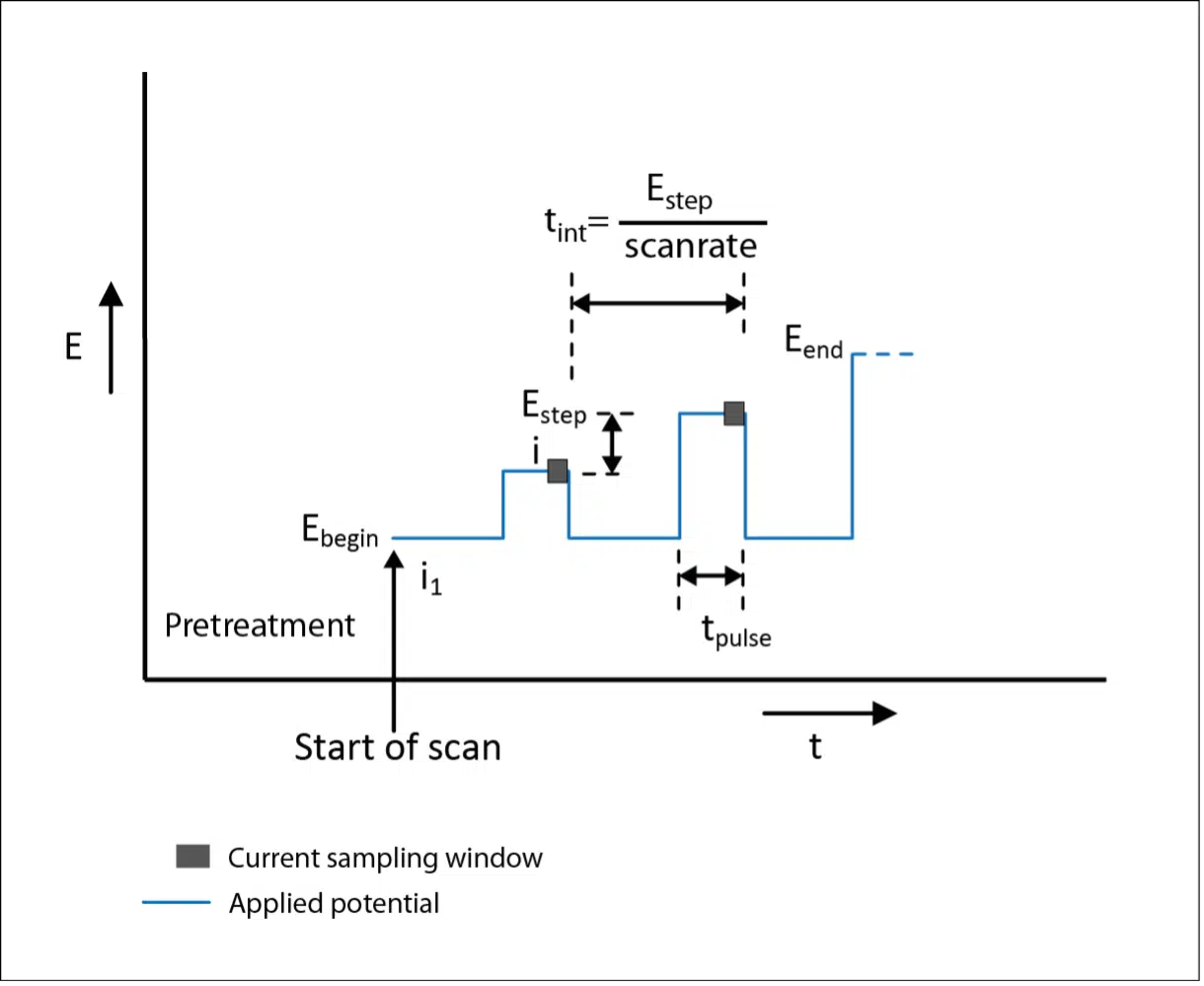
At the first potential step, the pulse is equal to E step, at next twice the value E step, until the end where the pulse is E begin + n * E step is equal to E end, where n = (E end – E begin) / E step + 1.
The pulse time t pulse is specified by the user, but must not exceed half the interval time.
So the t pulse <= E step / (scan rate * 2).