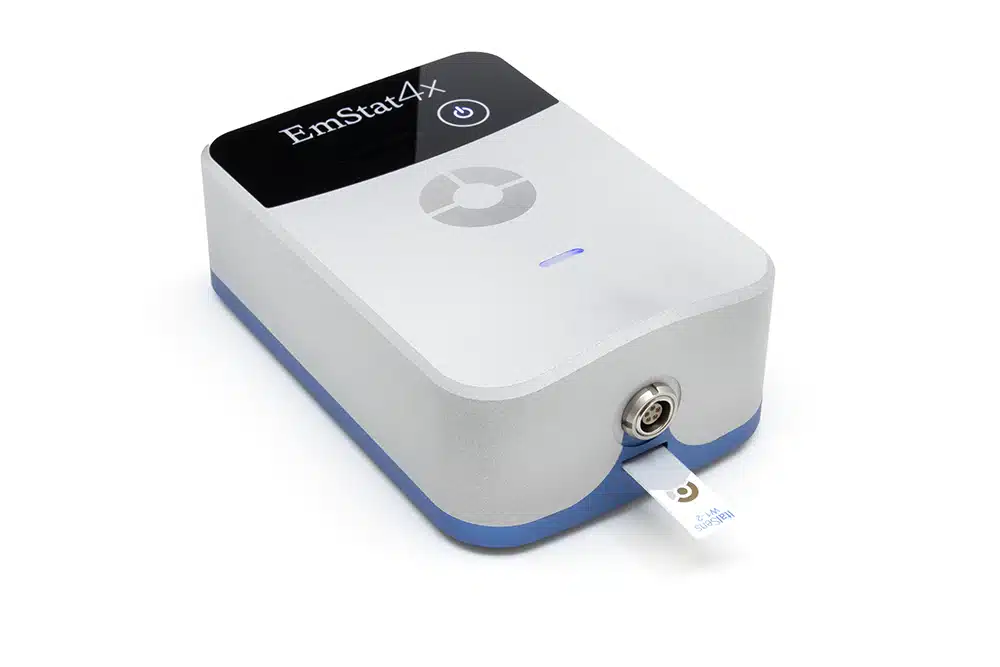
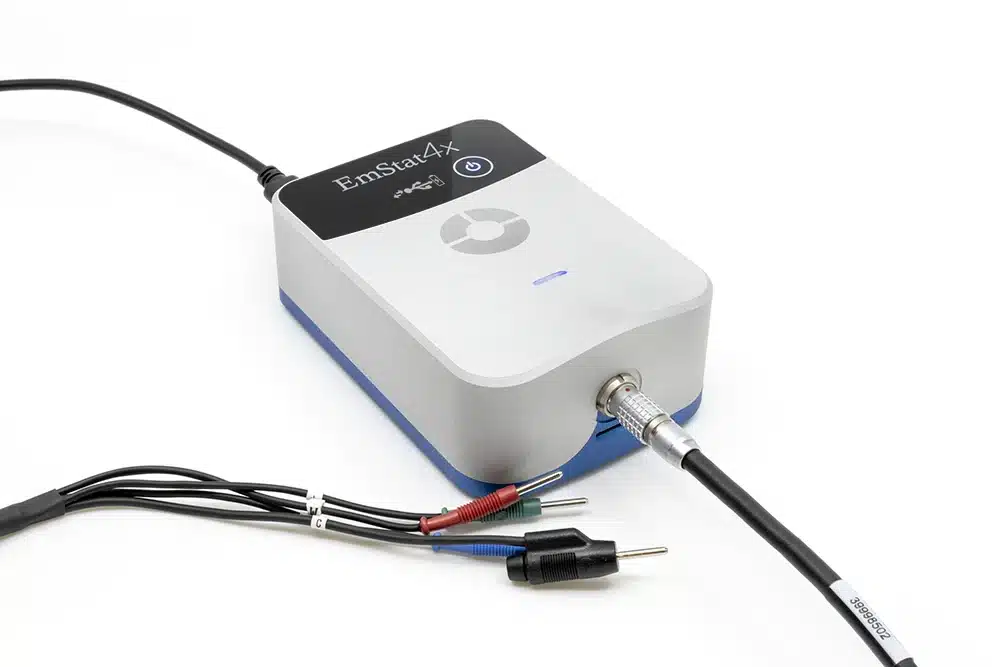
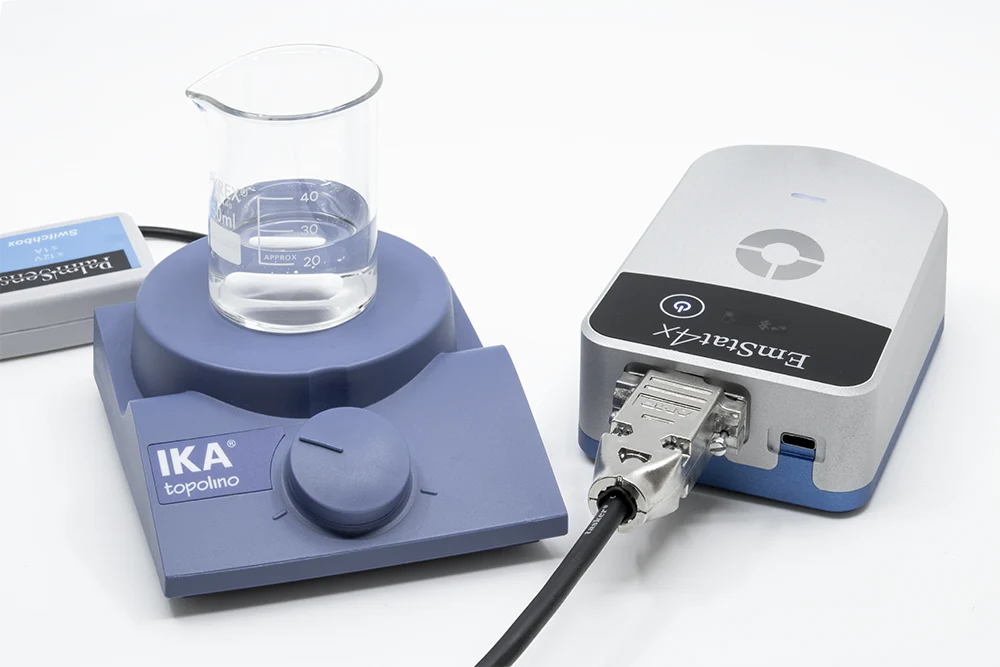
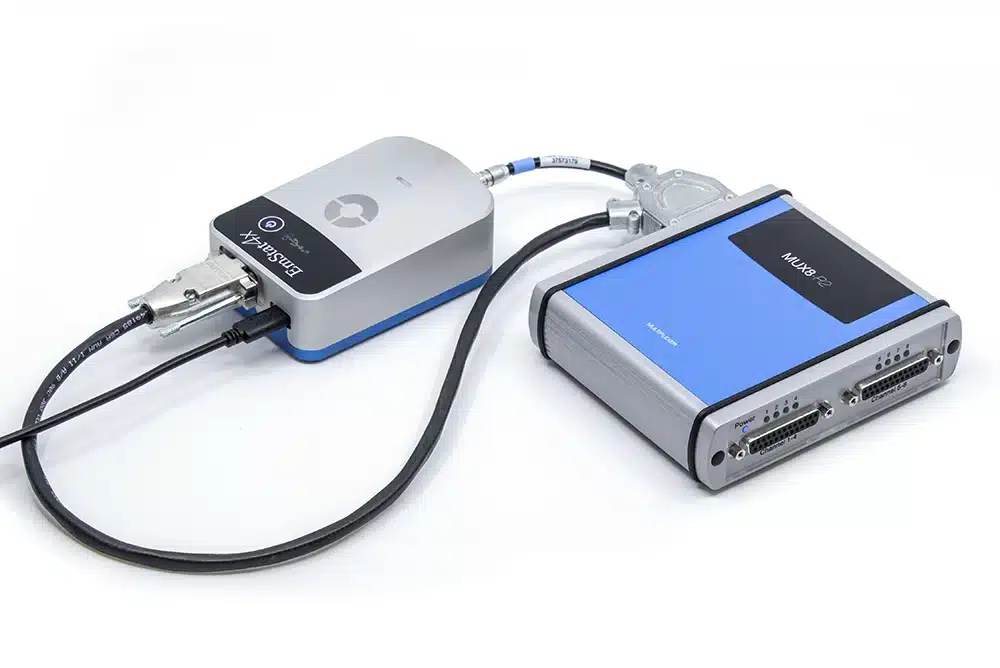
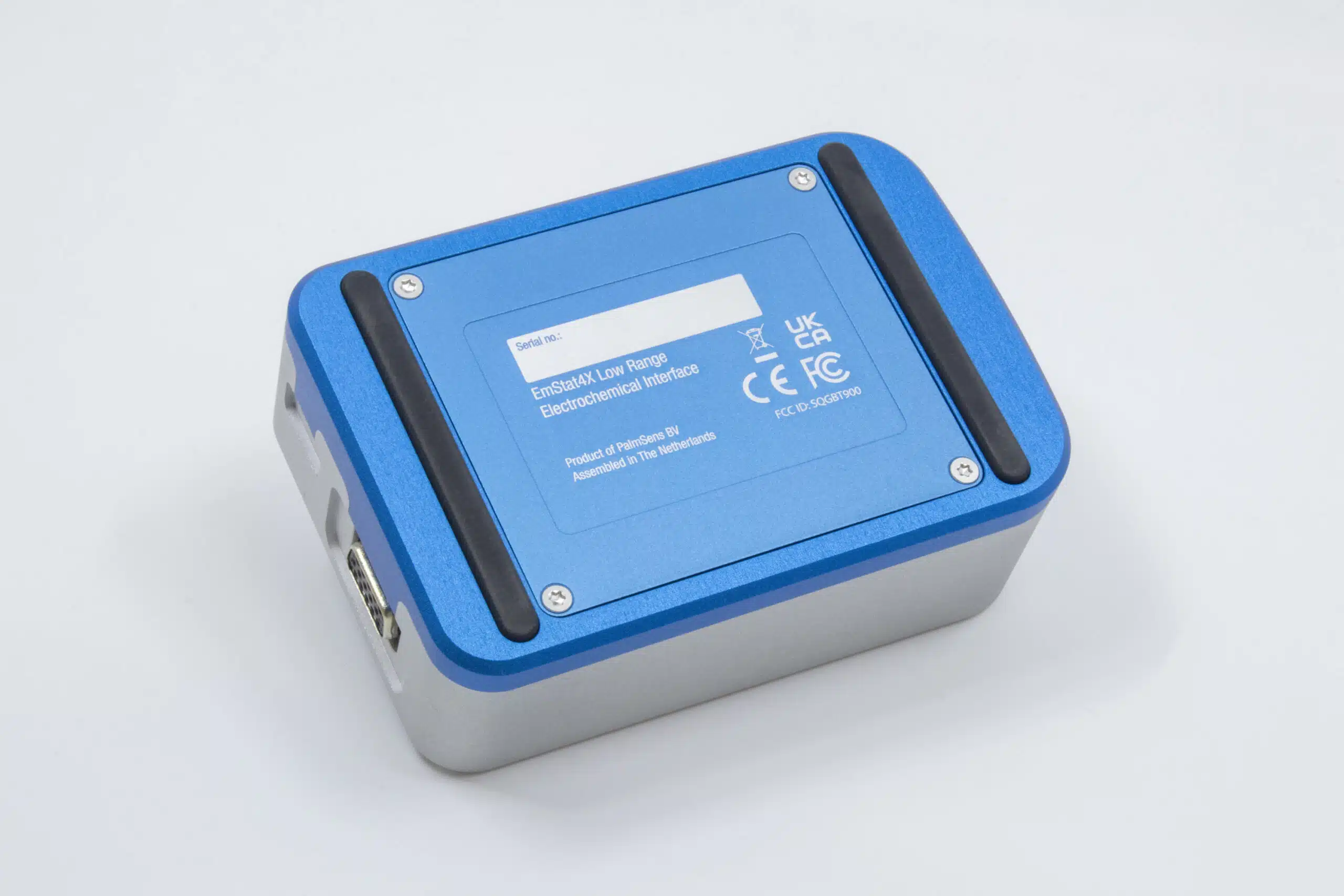
EmStat4X
High performance in a small footprint
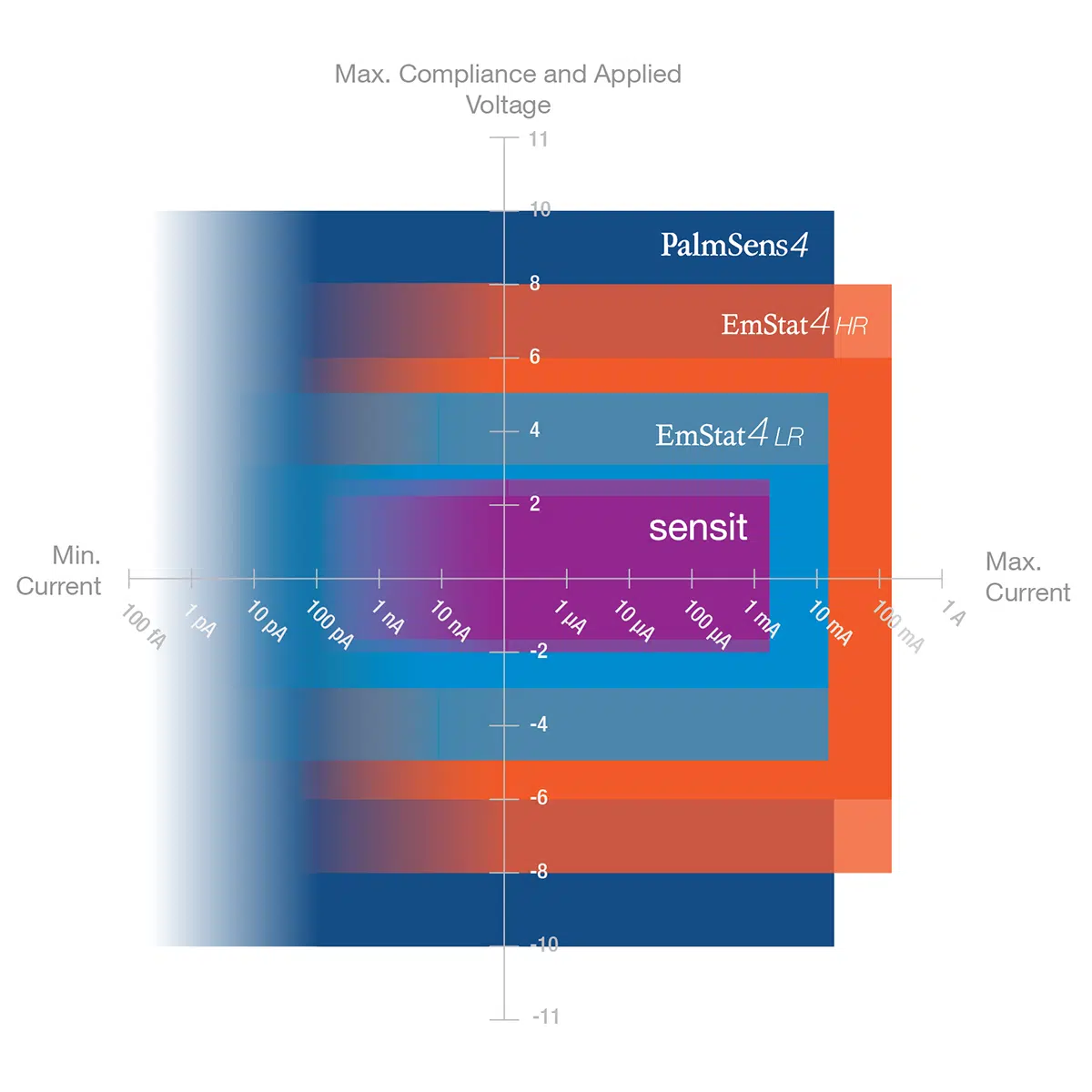
- Potential range ±3 V or ±6 V
- Max. current ±30 mA or ±200 mA
- Wireless control
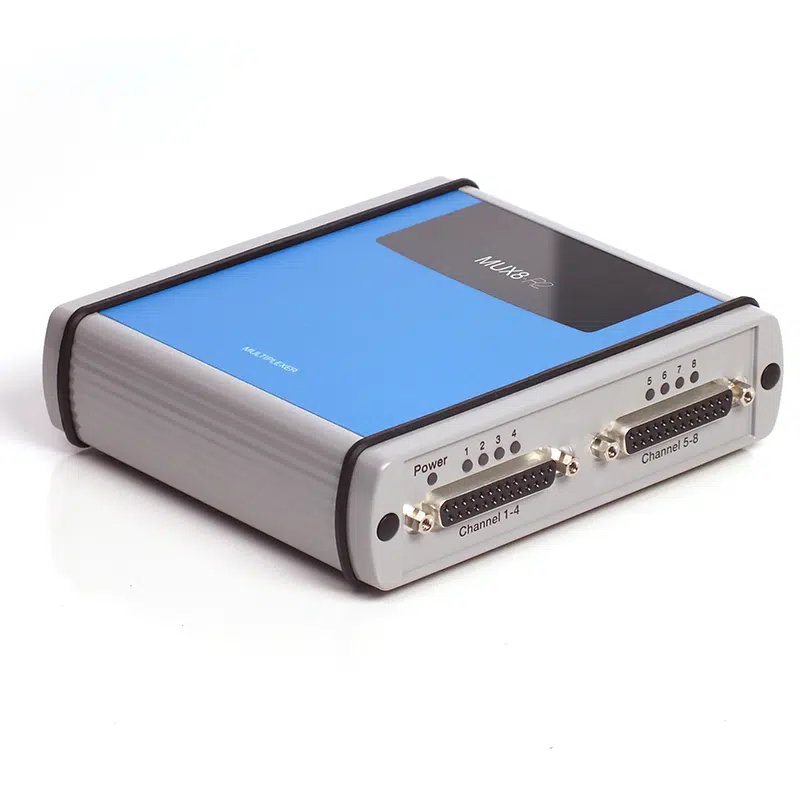
- Extendable with multiplexer
- iR compensation
Description
The EmStat4X delivers high performance in a small footprint. The EmStat4X is a small battery and USB-powered Potentiostat, Galvanostat, and optional Frequency Response Analyser (FRA) for Electrochemical Impedance Spectroscopy (EIS). The EmStat4X Low Range (LR) version is great for applications that require measuring low currents down to picoamps, like (bio)sensor research. The High Range (HR) version is very suitable for applications that need a maximum current of up to 200 mA. The EmStat4X is controlled with PSTrace for Windows, or you can write your own MethodSCRIPT and control it from any platform or operating system.
The EmStat4X LR and HR features include:
- Fast EIS support: for running fixed-frequency EIS measurements at a very low interval of around 1 ms.
- Auxiliary Port: for connecting to a MUX8-R2 multiplexer, temperature sensor, pH sensor, stirrer control, triggering and more.
- iR compensation: to compensate for the iR drop between the Reference electrode and the outside of the double layer of the electrochemical cell.
- Wireless: for a wireless connection to a PC, smartphone or tablet
- 11.1 Wh battery: for more than 8 hours of continuous measurements (typical with the LR).
- Small borderless display: showing the state of the battery and connectivity.
Two versions
The EmStat4X comes in two different versions:
- Low Range: for lower currents and potentials (±30 mA / ±3 V applied / ±5 V compliance)
- High Range: for higher currents and potentials (±200 mA / ±6 V applied / ±8 V compliance)
Both versions can be configured with optional EIS/FRA up to 200 kHz.
See specifications for a detailed comparison between the LR and HR.
Always a backup
Always a backup
The EmStat4X is equipped with 500 MB internal storage memory for storing your measurements as a backup. All internally stored measurements can be browsed and transferred back to the PC easily using the PSTrace software for Windows. Your data is always with your instrument wherever you take it.Standard included
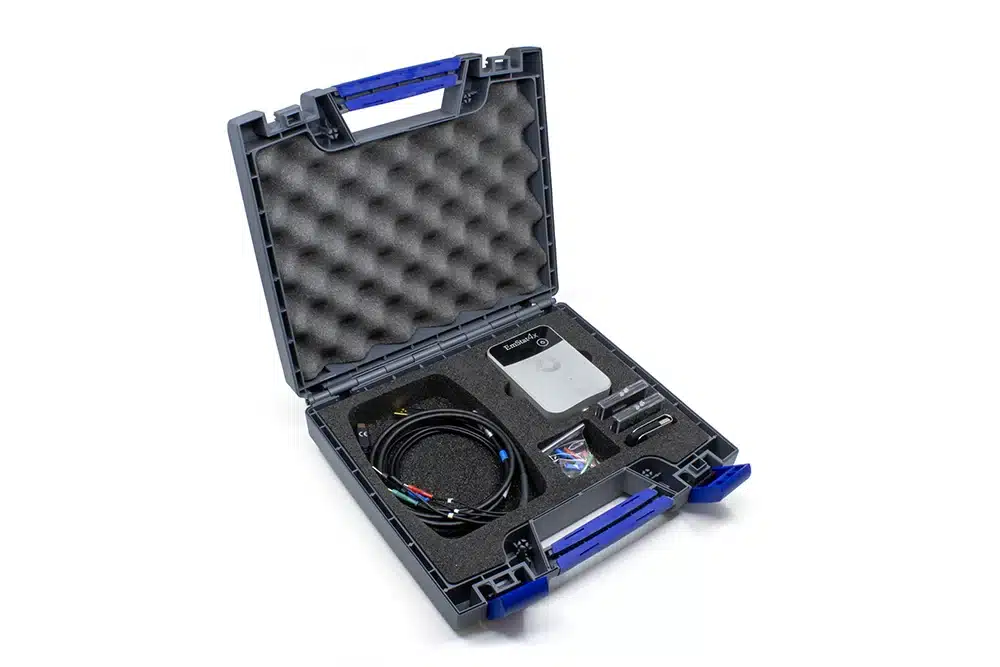
A standard EmStat4X includes a rugged carrying case with:
- EmStat4X LR or HR
- USB-C cable
- Cell cable: high quality, double-shielded cable with 2 mm banana connectors for Working, Counter, Reference electrode and Ground, 1 meter long
- 4 or 5 crocodile clips
- Dummy Cell
Also included:
- PSTrace software for Windows (on USB drive)
- Manual (hardcopy)
- Quick Start (hardcopy)
- Calibration report
Specifications
The EmStat4X is available in two versions: the LR (Low Range) and HR (High Range) version.
| Main differences between the EmStat4X Low and High Range | ||
|---|---|---|
 |
 |
|
|
|
||
| Potential range | ±3 V | ±6 V |
| Max. compliance voltage
The compliance voltage is the maximum voltage that can be applied between the working and counter electrode. Another name could be the maximum cell potential. Continue reading
|
±5 V | ±8 V |
| Current ranges | 1 nA to 10 mA (8 ranges) | 100 nA to 100 mA (7 ranges) |
| Max. current | ±30 mA | ±200 mA |
| Electrode connections | WE, RE, CE and ground, 2 mm banana plugs |
WE, RE, CE, Sense, and ground, 2 mm banana plugs |
| General | ||
|---|---|---|
| LR | HR | |
dc-potential range
The maximum potential difference, that can be applied between WE and RE.
|
±3 V | ±6 V |
compliance voltage
The compliance voltage is the maximum voltage that can be applied between the working and counter electrode. Another name could be the maximum cell potential. Continue reading
|
±5 V | ±8 V |
| maximum current | ±30 mA | ±200 mA |
| max. data acquisition rate | 1 000 000 samples /s | |
| control loop bandwidth (stability setting)
The range of frequencies between which you can measure. Continue reading
|
320 Hz, 3.2 kHz, 30 kHz or 570 kHz | |
| current follower bandwidth
The range of frequencies between which you can measure. Continue reading
|
23 Hz in 1 nA and 10 nA range 2.3 kHz in 100 nA and 1 uA range 230 kHz in 10 uA and 100 uA range > 500 kHz in ranges 1 mA and higher |
|
| Potentiostat | ||
|---|---|---|
| LR | HR | |
| applied potential resolution | 100 µV | 183 µV |
applied potential accuracy
The applied potential accuracy describes how close to the real values your applied potential is.
|
≤ 0.2% ±1 mV offset | |
current ranges
A potentiostat measures current. For optimal precision, the range between which currents are measured is split into multiple current ranges. A current range defines the maximum current a potentiostat can measure in a certain range. This means it will also determine the resolution, because the number of bits or rather states is fixed, while the current range is variable.
|
1 nA to 10 mA 8 ranges |
100 nA to 100 mA 7 ranges |
measured current resolution
The lowest observable difference between two values that a measurement device can differentiate between.
|
0.009% of CR (92 fA on 1 nA range) | 0.009% of CR (9.2 pA on 100 nA range) |
| measured current accuracy
The current accuracy describes how close to the real values your measured current is.
|
< 0.2% of current ±20 pA ±0.2% of range |
< 0.2% of current ±0.2% of range |
| Galvanostat | ||
|---|---|---|
| LR | HR | |
current ranges
A potentiostat measures current. For optimal precision, the range between which currents are measured is split into multiple current ranges. A current range defines the maximum current a potentiostat can measure in a certain range. This means it will also determine the resolution, because the number of bits or rather states is fixed, while the current range is variable.
|
10 nA, 1 uA, 100 uA, 10 mA 4 ranges |
1 uA, 100 uA, 10 mA, 100 mA 4 ranges |
| applied dc-current | ±3 * CR (current range) | |
| applied dc-current resolution | 0.01% of CR | 0.0183% of CR |
| applied dc- current accuracy
The current accuracy describes how close to the real values your measured current is.
|
< 0.4% of current ±20 pA ±0.2% of range |
< 0.4% of current ±0.2% of range |
| potential ranges |
50 mV, 100 mV, 200 mV, 500 mV, 1 V |
|
| measured dc-potential resolution |
96 µV at ±3 V (1 V range) |
193 µV at ±6 V (1 V range) |
| measured dc-potential accuracy | ≤ 0.2% potential ±1 mV offset | |
| FRA / EIS | ||
|---|---|---|
| LR | HR | |
| frequency range | 10 µHz to 200 kHz | |
| ac-amplitude range |
1 mV to 900 mV rms, or 2.5 V p-p |
|
| measured current accuracy
The current accuracy describes how close to the real values your measured current is.
|
≤ 0.2% at Full Scale Range | |
| GEIS | ||
|---|---|---|
| LR | HR | |
| frequency range | 10 µHz to 100 kHz | |
| ac-amplitude range |
0.9 * CR (Arms) |
|
| Electrometer | ||
|---|---|---|
| LR | HR | |
electrometer amplifier input
The amplifier input resistance of the amplifier in the electrometer determines the load that the amplifier places on the source of the signal being fed into it. Ideally the resistance is infinite, and the load to be zero to not to influence your measurement.
|
> 1 TΩ // 10 pF | |
bandwidth
The range of frequencies between which you can measure. Continue reading
|
500 kHz |
|
| iR compensation | ||
|---|---|---|
| method used for iR-drop compensation | Positive Feedback | |
| resolution of MDAC used for correcting potential |
12-bit |
|
| Max. compensated resistance |
1 MOhm |
|
| Other | ||
|---|---|---|
| LR | HR | |
| electrode connections |
WE, RE, CE, |
WE, RE, CE, S |
| power consumption |
Typical: 1W (idle) |
Typical: 1.5W (idle) |
| battery |
11.1 Wh capacity |
|
| power source |
USB-C or internal LiPo battery |
|
| communications |
USB-C or Wireless |
|
| housing |
aluminum body: |
|
| weight |
~500 g |
|
| internal storage space |
500 MB, equivalent to > 15M datapoints |
|
| Auxiliary port (D-Sub 15) | |
|---|---|
| analog input | ±10 V, 16-bit |
| analog output | 0-6 V, 12 bit |
| 4 digital outputs | 0-3.3 V |
| 1 digital input | 0-3.3 V |
| i-out and E-out | raw output of current and potential E-out ±5 V (LR) ±8 V (HR) i-out ±3 V |
| power | 5 V output (max. 300 mA) |
| EmStat4X LR EIS Accuracy Contour Plot |
|---|
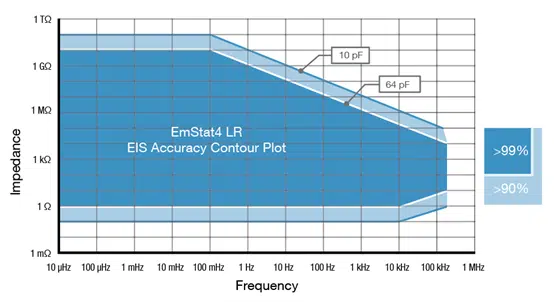
Note The accuracy contour plots were determined with an ac-amplitude of ≤10 mV rms for all limits, except for the high impedance limit, which was determined using an ac-amplitude of 250 mV. The standard cables were used. Please note that the true limits of an impedance measurement are influenced by all components in the system, e.g. connections, the environment, and the cell. |
| EmStat4X HR EIS Accuracy Contour Plot |
|---|
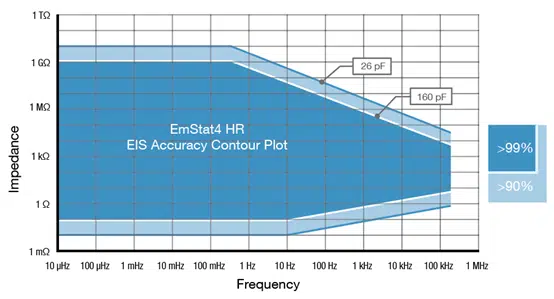
Note The accuracy contour plots were determined with an ac-amplitude of ≤10 mV rms for all limits, except for the high impedance limit, which was determined using an ac-amplitude of 250 mV. The standard cables were used. Please note that the true limits of an impedance measurement are influenced by all components in the system, e.g. connections, the environment, and the cell. |
Accessories
Accessories for EmStat4X
You may also like…
Software
PSTrace
PSTrace for Windows provides support for all techniques and device functionalities. With a smooth simple interface, showing only the applicable controls, PSTrace is suitable for all levels of user experience. Functions include:
- Direct validation of method parameters
- Equivalent Circuit Fitting
- Automated peak search
- Scripting for running an automated sequence of measurements
- Open data in Origin and Excel with one click of a button
- Load data from the internal storage
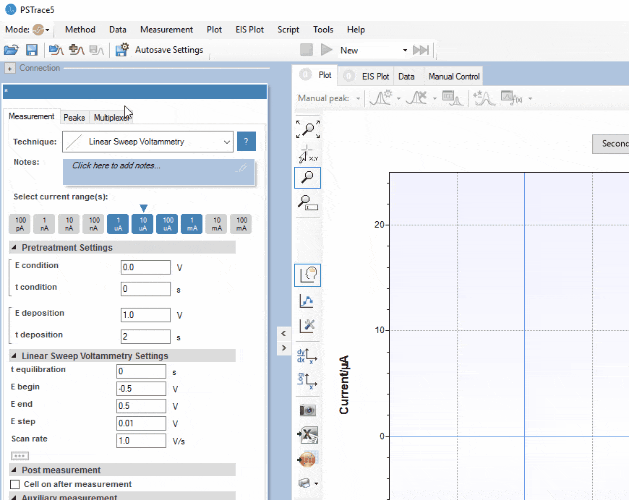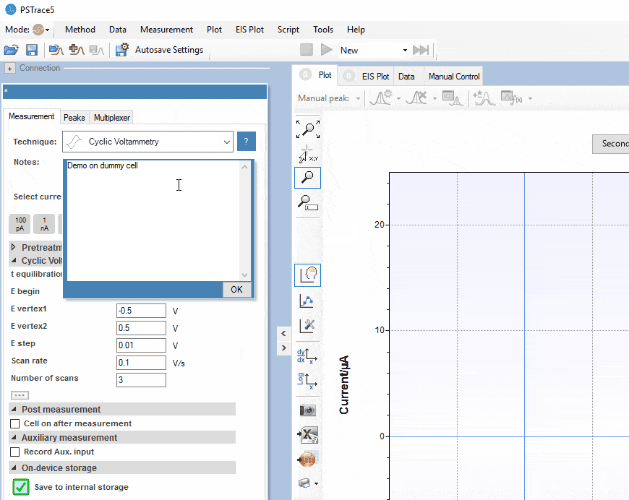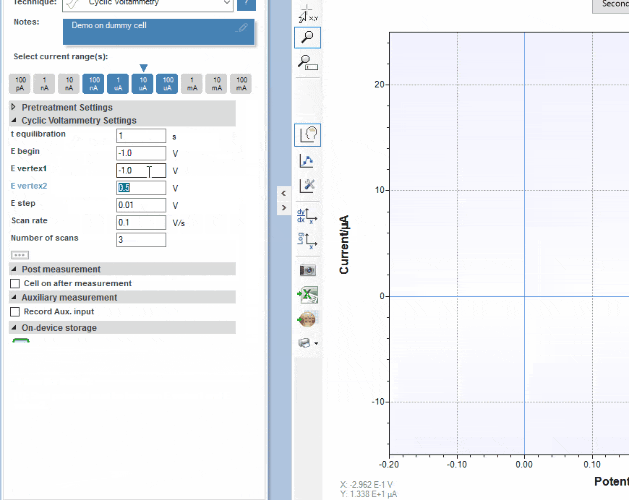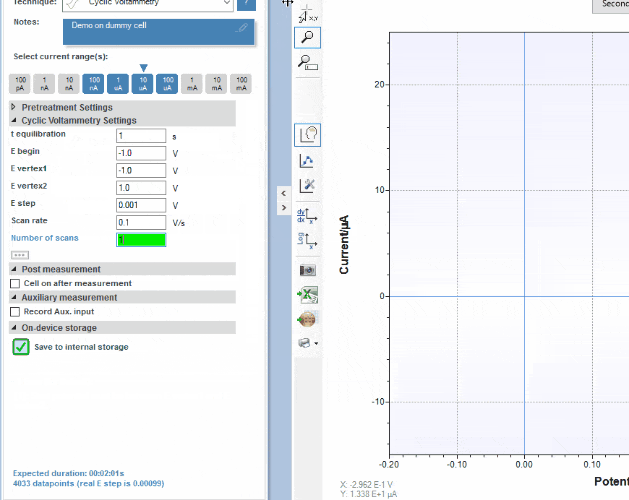
Software Development Kits
The PalmSens Software Development Kits (SDKs) for .NET can be used with any of our instruments or OEM potentiostat modules to develop your own software. The SDK’s come with a set of examples that shows how to use the libraries.
PalmSens SDKs with examples are available for the following .NET Frameworks:
- WinForms
- WPF
- Xamarin (for Android)
MethodSCRIPT™ communications protocol
The potentiostat (module) has an on-board parser for the MethodSCRIPT™ scripting language. This language allows developers to program a human-readable script for the potentiostat on any platform or operating system. The simple script language allows for running electrochemical techniques supported by EmStat4 and makes it easy to combine different measurements and other tasks.

Downloads
Other (1)
| Name | Last updated | |
|---|---|---|
| Serial USB driver With this serial driver you can connect to for example the EmStat4X serially. This allows you tu use Python or TeraTerm. To install the driver: Unzip the driver, right click on palmsens_cdc.inf and click install. Go to your Windows device manager, and manually change the driver of the EmStat4X to use the USB Serial driver. The instrument will now have a COMXX as a name. In Python or TeraTerm, select 921600 bps as the baudrate for the EmStat4. | 01-04-25 |
Documentation (4)
| Name | Last updated | |
|---|---|---|
| EmStat4X Brochure Overview of all specifications and supported electrochemical techniques. | 08-01-25 | |
| MethodSCRIPT v1.5 The MethodSCRIPT scripting language is designed to improve the flexibility of the PalmSens potentiostat and galvanostat devices for OEM users. It allows users to start measurements with arguments that are similar to the arguments in PSTrace. PalmSens provides libraries and examples for handling low level communication and generating scripts for MethodSCRIPT devices such as the EmStat Pico and EmStat4. | 25-03-24 | |
| EmStat4M Communication Protocol V1.3 Describes how to communicate with the EmStat4M directly and how to send MethodSCRIPTS. | 25-03-24 | |
| EmStat4X Operator’s Manual Learn how to connect the instrument, understand the specifications, use the features and troubleshoot if needed. | 13-03-24 |
Software (1)
| Name | Last updated | |
|---|---|---|
| PSTrace PC software for all single channel instruments PSTrace software is shipped as standard with all single channel and multiplexed instruments. The software provides support for all techniques and device functionalities. | 08-07-24 |