Description
This EIS Plus Corrosion Package includes everything you need to get started with corrosion measurements.
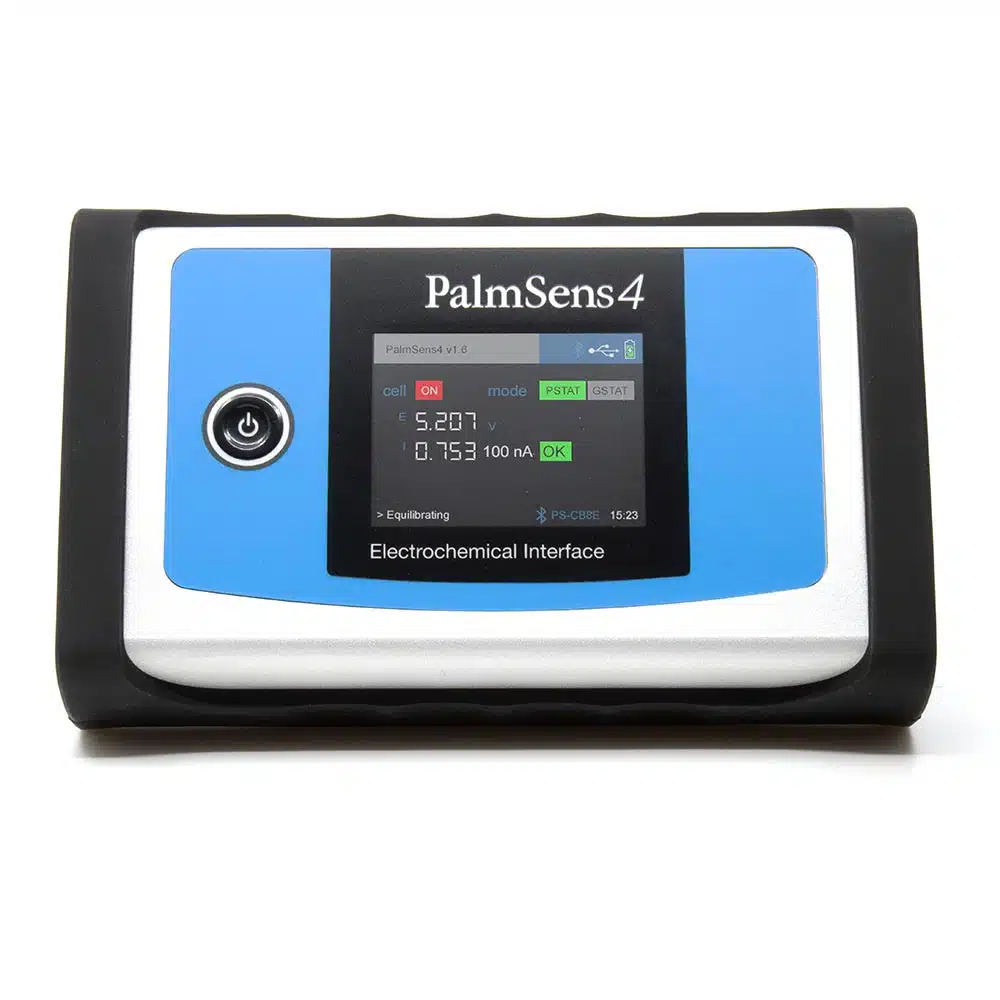
The included instrument is the PalmSens4 which is a USB and battery-powered Potentiostat, Galvanostat, and Electrochemical Impedance Spectroscopy (EIS) analyzer. The PalmSens4 has a large potential range (-10V to 10V) and current range (100 pA to 10 mA) with a high resolution and low noise. This instrument is a complete laboratory instrument but its compact and rugged design makes it also ideal for fieldwork.
PalmSens4 allows for a wide range of corrosion analysis methods; polarization curves to extract the Tafel slopes, corrosion rates, corrosion current, apply a current to the surface for electroplating, deposit films, or force corrosion to happen. Additionally, you can perform EIS (Electrochemical Impedance Spectroscopy) from 0.1 µHz to 1 MHz, which will allow you to extract the coating resistance, the polarization resistance, the pore resistance, the coating capacitance, water uptake of a coating and to estimate the time to failure (TTF). The instrument comes with PSTrace5 software which allows for different corrosion analytical techniques for automatic or manual analysis.
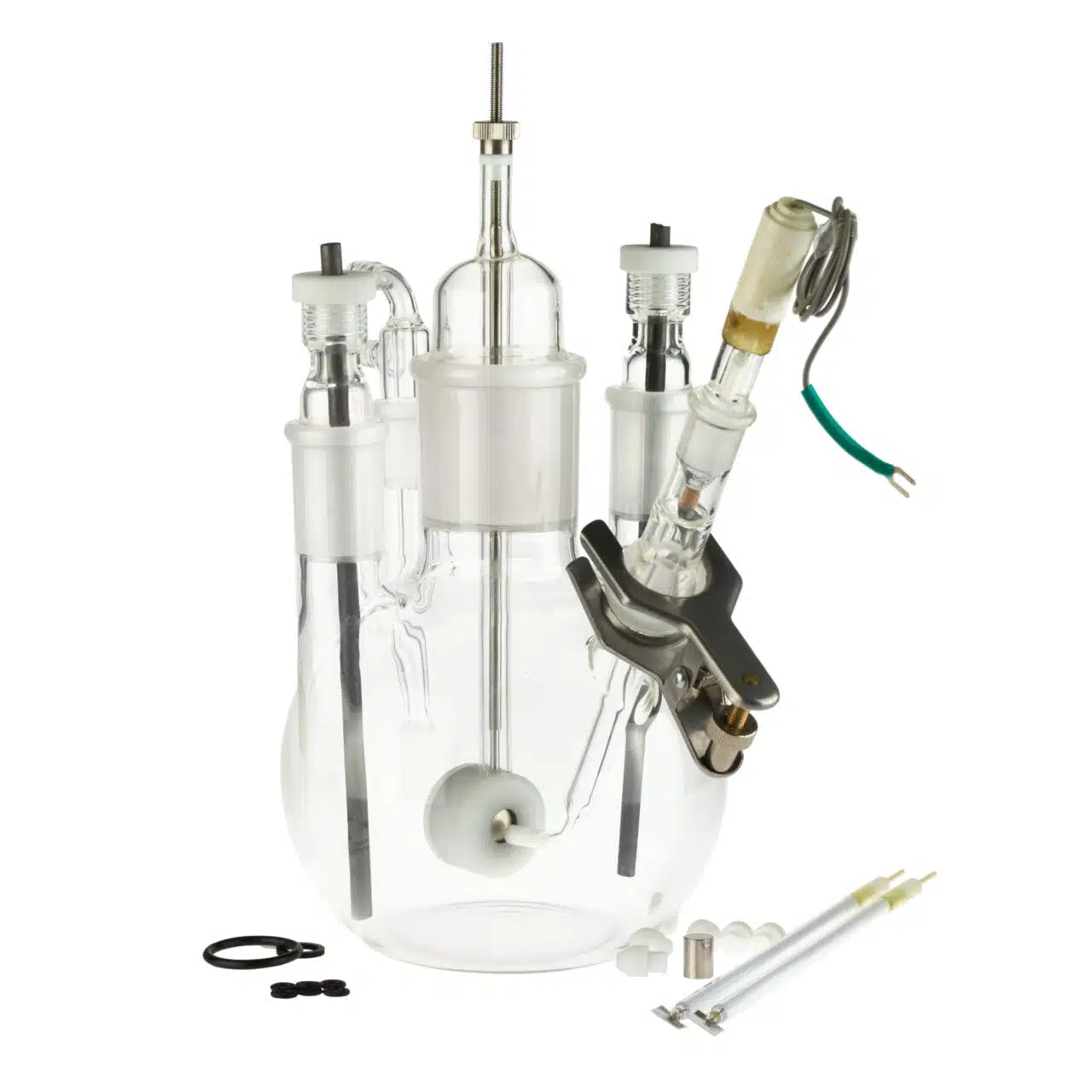
Together with our Corrosion Handbook and the Corrosion Cell Kit, it makes a good combination to get going with electrochemical corrosion studies.
Standard included with an EIS Plus Corrosion Package
- Corrosion Cell
- Corrosion Handbook
- PalmSens4
- Rugged carrying case
- High quality, double shielded cell cable with 2 mm banana connectors for Working, Counter, Reference electrode, Sense and Ground
- Crocodile clips
- USB cable
- Manual and Quick Start document
- PSTrace software for Windows
Specifications
| General | |
|---|---|
dc-potential range
The maximum potential difference, that can be applied between WE and RE.
|
±10 V (or ±5 V) * |
compliance voltage
The compliance voltage is the maximum voltage that can be applied between the working and counter electrode. Another name could be the maximum cell potential. Continue reading
|
±10 V |
| maximum current | ±30 mA (typical) |
| max. acquisition rate | 150,000 data points/s |
| * depending on PalmSens4 hardware configuration | |
| Potentiostat (controlled potential mode) | |
|---|---|
applied dc-potential resolution
The lowest observable difference between two values that a measurement device can differentiate between.
|
76.3 µV ( 18-bit )
A potentiostat has to convert real-world measurements into a binary format to use them. The number of bits the real world measurement is converted to, is one of the determining factors for the resolution of a potentiostat. A potentiostat with 18 bits, can measure the potential and current in 2^18 or roughly 262 thousand different steps. Continue reading
|
applied potential accuracy
The applied potential accuracy describes how close to the real values your applied potential is.
|
≤ 0.1% ±1 mV offset |
current ranges
A potentiostat measures current. For optimal precision, the range between which currents are measured is split into multiple current ranges. A current range defines the maximum current a potentiostat can measure in a certain range. This means it will also determine the resolution, because the number of bits or rather states is fixed, while the current range is variable.
|
100 pA to 10 mA (9 ranges) |
current accuracy
The current accuracy describes how close to the real values your measured current is.
|
≤ 0.1 % (at Full Scale Range) |
measured current resolution
The lowest observable difference between two values that a measurement device can differentiate between.
|
0.005 % of current range ( 18-bit , 5 fA on 100 pA range)
A potentiostat has to convert real-world measurements into a binary format to use them. The number of bits the real world measurement is converted to, is one of the determining factors for the resolution of a potentiostat. A potentiostat with 18 bits, can measure the potential and current in 2^18 or roughly 262 thousand different steps. Continue reading
0.0025% of 10 mA range |
| Galvanostat (controlled current mode) | |
|---|---|
current ranges
A potentiostat measures current. For optimal precision, the range between which currents are measured is split into multiple current ranges. A current range defines the maximum current a potentiostat can measure in a certain range. This means it will also determine the resolution, because the number of bits or rather states is fixed, while the current range is variable.
|
1 nA to 10 mA (8 ranges) |
| applied dc-current range | ±6 times applied current range |
| applied dc-current resolution | 0.0076% of applied current range (<10 mA) 0.0038% of 10 mA range |
| measured dc-potential resolution | 78.13 μV at ±10 V (gain 1, 18-bit )
A potentiostat has to convert real-world measurements into a binary format to use them. The number of bits the real world measurement is converted to, is one of the determining factors for the resolution of a potentiostat. A potentiostat with 18 bits, can measure the potential and current in 2^18 or roughly 262 thousand different steps. Continue reading
7.813 μV at ±1 V (gain 10) 0.7813 μV at ±0.1 V (gain 100) |
| measured dc-potential accuracy | ≤ 0.05% or ±1 mV (for |E| < ±9 V) ≤ 0.2% (for |E| ≥ ±9 V) |
| FRA / EIS (impedance measurements) | |
|---|---|
| frequency range | 10 μHz to 1 MHz (or 10 μHz to 100 kHz) * |
| ac-amplitude range | 1 mV to 0.25 V rms, or 0.7 V p-p |
| * depending on PalmSens4 hardware configuration | |
| GEIS (galvanostatic impedance measurements) | |
|---|---|
| frequency range | 10 μHz to 100 kHz (or 10 μHz to 100 kHz) |
| ac-amplitude range | 0.001 x CR to 0.4 x CR (<10 mA) 0.001 x CR to 0.2 x CR (10 mA) (CR = current range) |
| Electrometer | |
|---|---|
electrometer amplifier input
The amplifier input resistance of the amplifier in the electrometer determines the load that the amplifier places on the source of the signal being fed into it. Ideally the resistance is infinite, and the load to be zero to not to influence your measurement.
|
> 1 TΩ // 10 pF |
bandwidth
The range of frequencies between which you can measure. Continue reading
|
1 MHz |
| Other | |
|---|---|
| housing | aluminium with rubber sleeve: 15.7 x 9.7 x 3.5 cm3 |
| weight | +/- 500 g |
| temperature range | 0 ºC to + 50 ºC |
| power supply | USB or internal LiPo battery |
| communication | USB and Wirelessly (Dual Mode) |
| battery time | > 16 hours idle time > 4 hours with cell on at max. current extendable by means of power bank |
| internal storage space | 8 GB or +/- 800000 measurements incl. method info (assuming 200 data points per measurement) |
| Auxiliary port (D-Sub 15) | |
|---|---|
| analog input | ±10 V, 18-bit
A potentiostat has to convert real-world measurements into a binary format to use them. The number of bits the real world measurement is converted to, is one of the determining factors for the resolution of a potentiostat. A potentiostat with 18 bits, can measure the potential and current in 2^18 or roughly 262 thousand different steps. Continue reading
|
| analog output | 0-10 V, 12 bit (1 kOhm output impedance) |
| 4 digital outputs | 0-5 V |
| 1 digital input | 0-5 V |
| i-out and E-out | raw output of current and potential E-out ±10 V (1 kOhm output impedance) i-out ±6 V (1 kOhm output impedance) |
| power | 5 V output (max. 150 mA) |
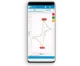
| EIS Accuracy Contour Plot | |
|---|---|
 |
|
Software
PSTrace corrosion mode
PSTrace for Windows has a special Corrosion mode, in which it provides support for all common corrosion techniques and device functionalities. With a smooth simple interface, showing only the applicable controls, PSTrace is suitable for all levels of user experience. Functions include:
- Tafel analysis
- Determine Corrosion Potential and Current
- Circuit fitting
- Determine Corrosion Rate
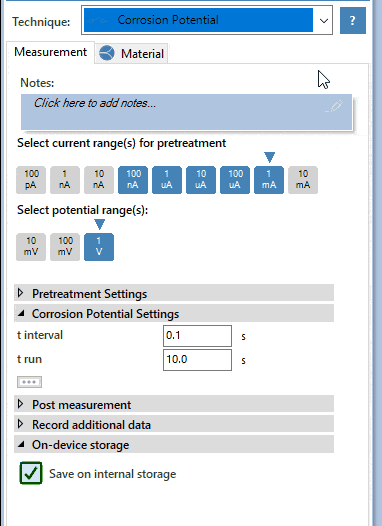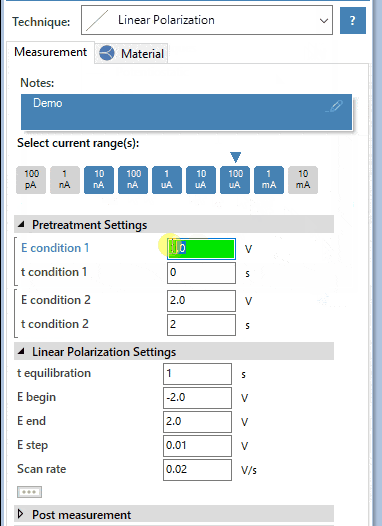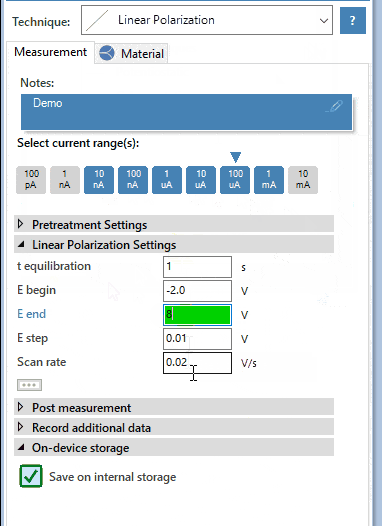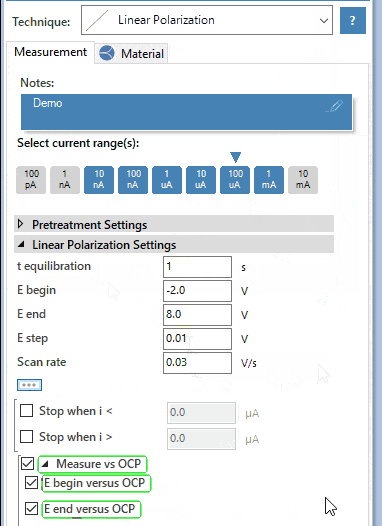
Tafel plot analysis
The exponential relationship between the applied current at a platinum surface and the potential plotted in a graph is known as a Tafel plot. PSTrace helps you fitting a Tafel plot and deriving the corrosion current and corrosion rate.
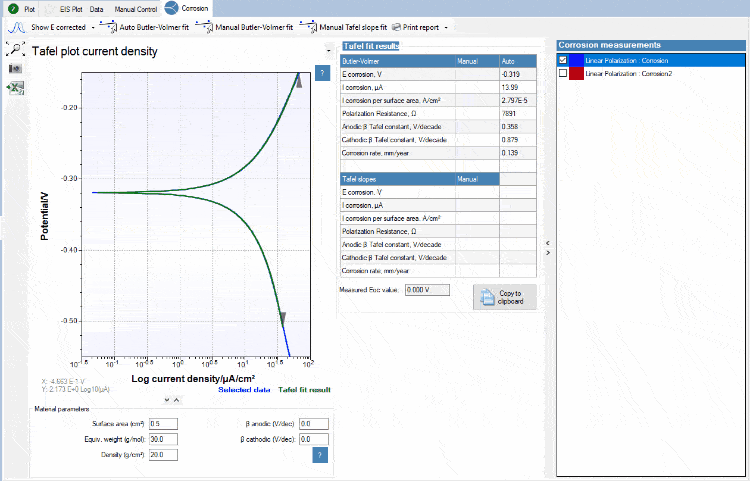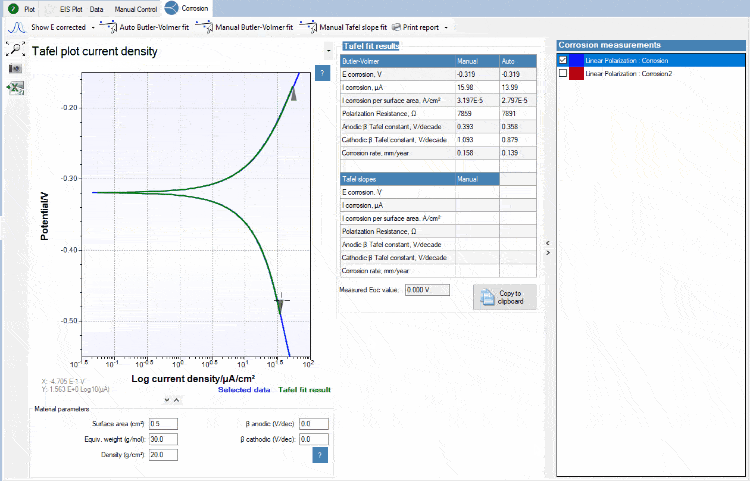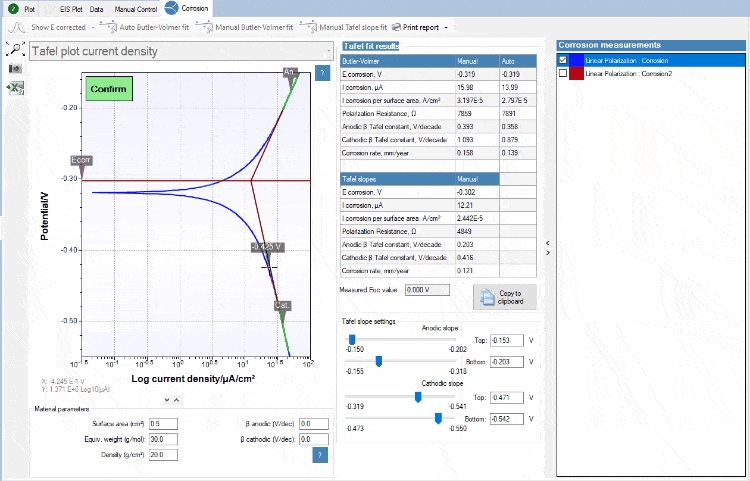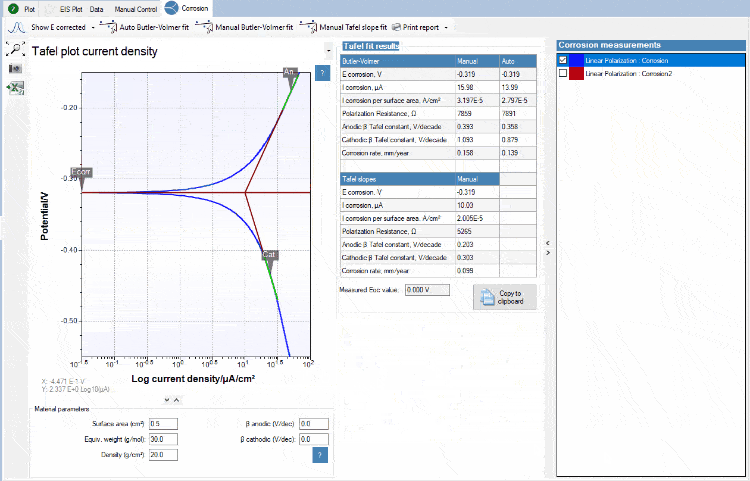
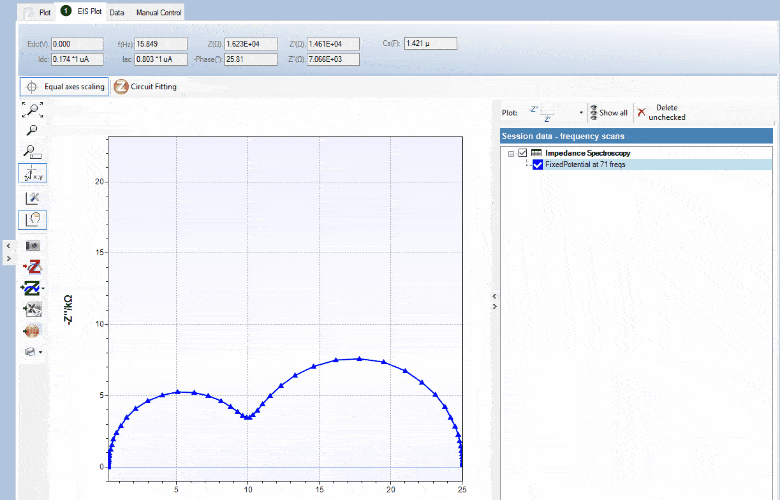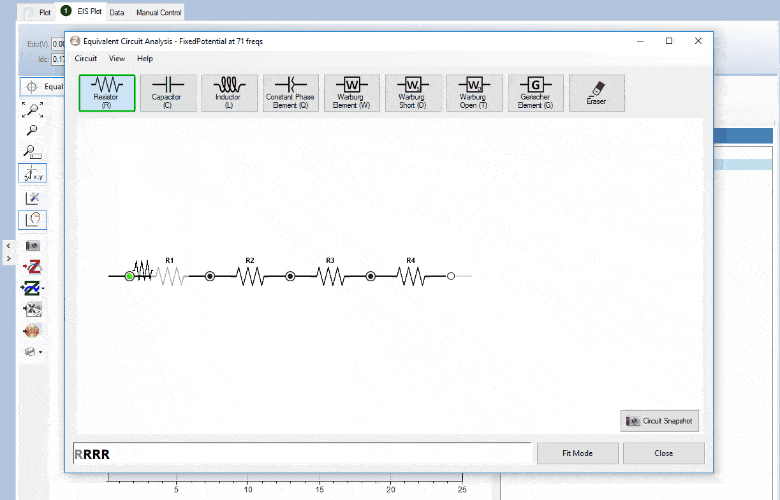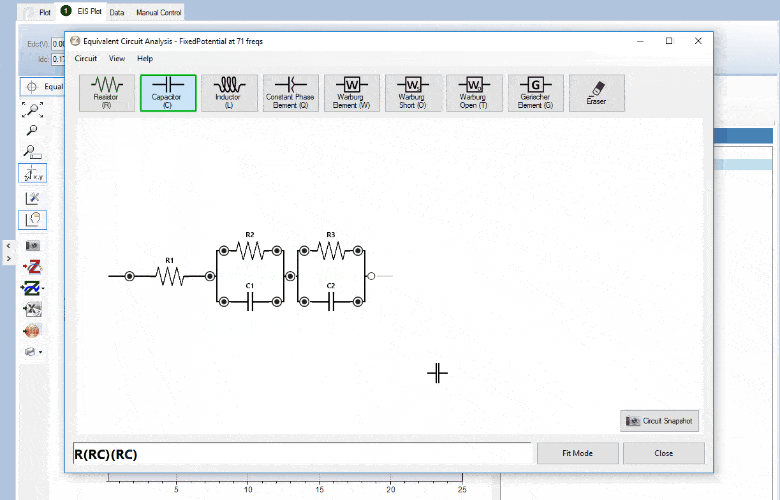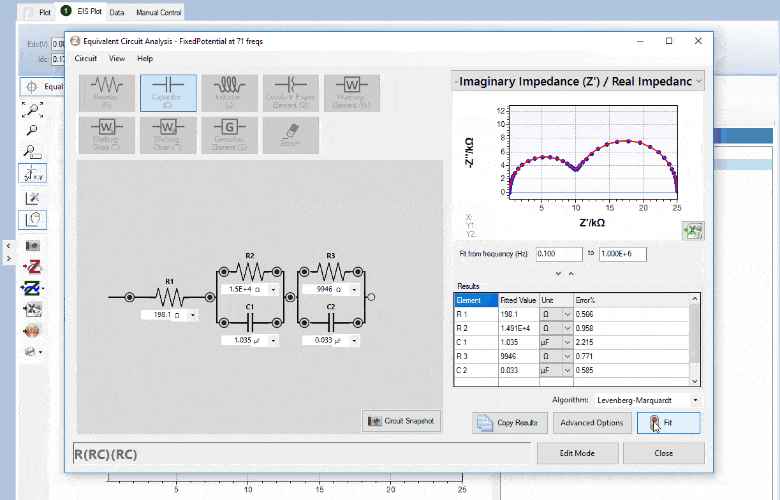
Circuit fitting
PSTrace supports Equivalent Circuit Fitting. Drawing your circuit and fitting your data has never been easier. The interface allows you to quickly draw or change the circuit design. The circuit and fitted data are automatically saved with your .pssession data file.
The circuit editor can be used in different modes;
- Edit mode; draw the circuit or type CDC circuit
- Fit mode; fit the EIS data on the circuit
- Simulation mode; run simulations on circuits
Downloads
| Name | Type | Last updated | |
|---|---|---|---|
| PSTrace PC software for all single channel instruments PSTrace software is shipped as standard with all single channel and multiplexed instruments. The software provides support for all techniques and device functionalities. | Software | 08-07-24 | |
| Corrosion Handbook Theory and practical advice for corrosion measurements. This handbook explains some basic knowledge of corrosion research with a focus on Linear Polarization Curves and Electrochemical Impedance Spectroscopy (EIS). Furthermore, it should afterward be possible to have a general idea of what can be read from the Tafel plot and the EIS spectrum. Typical shapes of curves and spectra will be shown, to develop some feeling for possible phenomena and indicators. | Documentation | 05-06-24 | |
| PalmSens4 Brochure PalmSens4 Brochure | Documentation | 28-02-23 | |
| Corrosion Cell Set contents This document specifies the contents of the Corrosion Cell Set, and contains an overview of the kit and the flat specimen holder. | Documentation | 02-06-21 |