Electrochemical techniques
Coulometric Detection
Coulometric Detection is an electrochemical technique during which a potential is set. This technique is usually called Chronocoulometry at PalmSens. The current is recorded and shown in a graph versus the time.
Potentiostatic Chronoamperometry
Potentiostatic Chronoamperometry is an electrochemical technique, usually called Chronoamperometry (CA) at PalmSens. Read all about it.

Constant Potential Chronoamperometry
Constant Potential Chronoamperometry is an electrochemical technique, usually called Chronoamperometry (CA) at PalmSens. Read all about it.

Potentiostatic DC Measurement
Potentiostatic DC Measurement is an electrochemical technique, usually called Chronoamperometry (CA) at PalmSens. Read all about it.

Amperometric i-t Curve (i-t)
An amperometric i-t Curve (i-t) is an electrochemical technique, usually called Chronoamperometry (CA) at PalmSens. Read all about it.

Potentiostatic Polarization
Potentiostatic Polarization is an electrochemical technique, usually called Chronoamperometry (CA) at PalmSens. Read all about it.
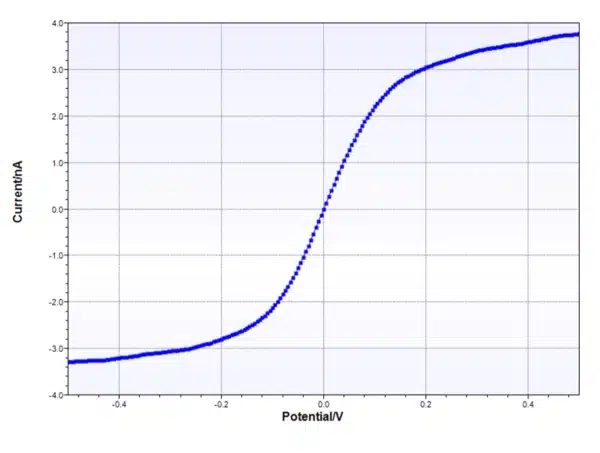
Reverse Normal Pulse Voltammetry
Reverse Normal Pulse Voltammetry is an electrochemical technique, usually called Normal Pulse Voltammetry at PalmSens. With Reverse Normal Pulse Voltammetry the influence of diffusion limitation on your I-E curve (Cottrel behavior) is removed.
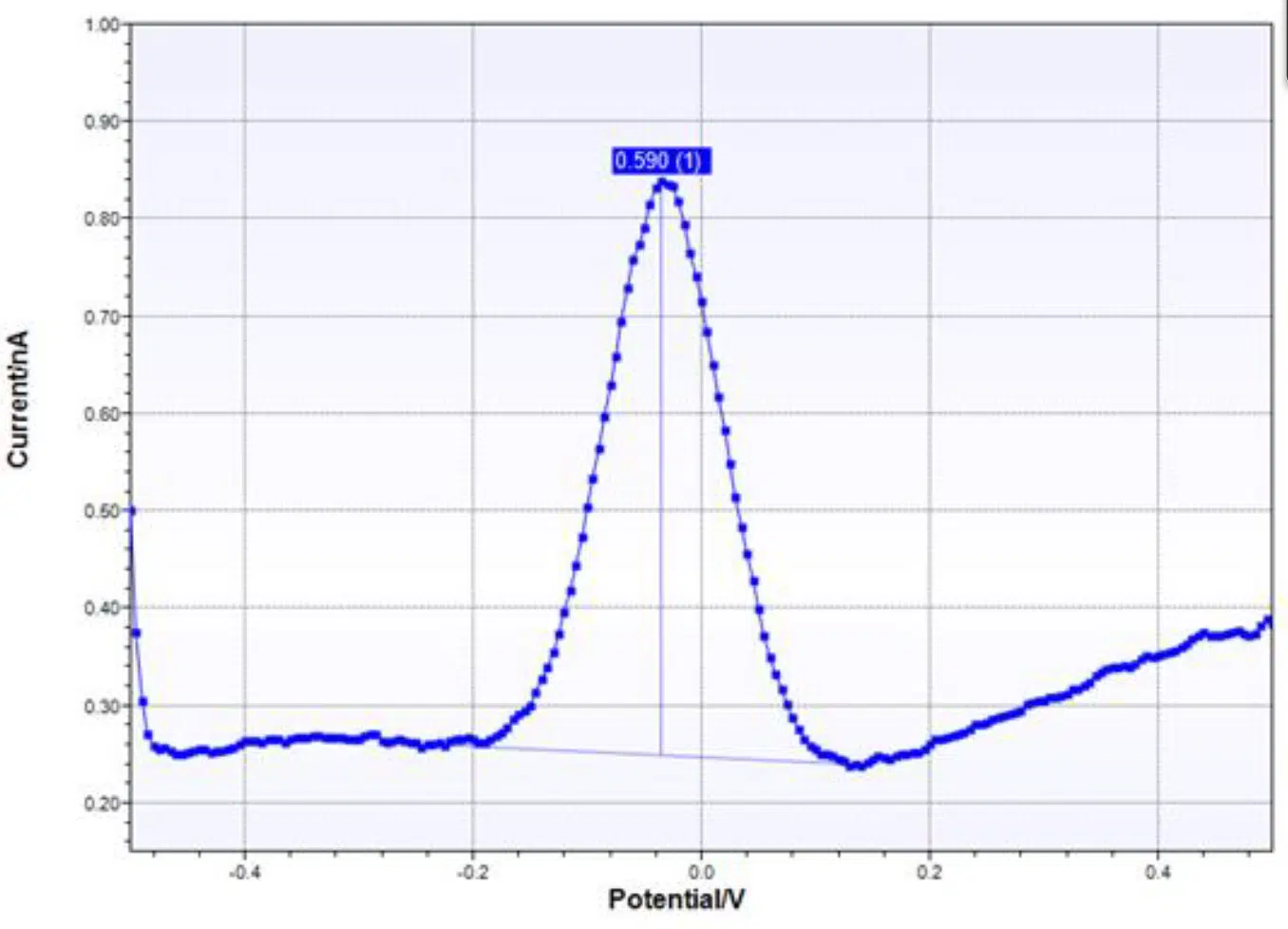
Pot. Differential Pulse
Pot. Differential Pulse is an electrochemical technique commonly called Differential Pulse Voltammetry at PalmSens.

Differential Pulse Polarography
Differential Pulse Polarography is an electrochemical technique commonly called Differential Pulse Voltammetry at PalmSens. ...
Amperometric Detection
Amperiometric Detection or Chronoamperometry (CA) is a simple, widely used electrochemical measurement technique. Many sensors, like those for glucose or oxygen, require this technique.
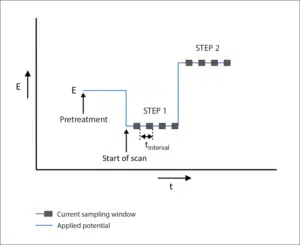
Potentiometric stripping analysis
Potentiometric stripping analysis is a sensitive analytical technique. Before the SCP measurement starts a deposition stage at the deposition potential E dep is required. After th...
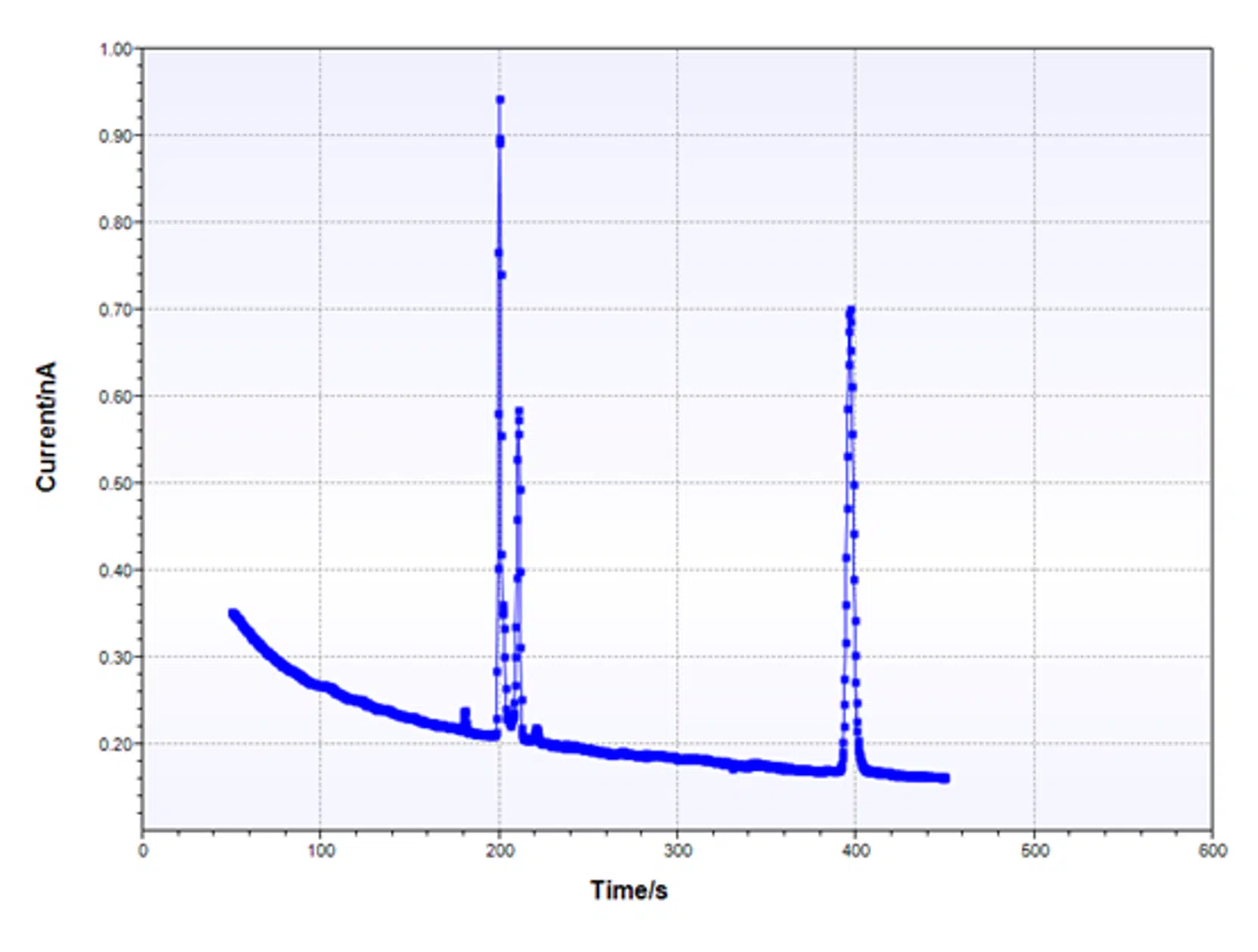
Chrono methods high speed (∆t > 100 ns)
Chrono methods high speed (∆t > 100 ns) is a form of amperometric detection with very high sampling rates or respectively very short interval times. At PalmSens is is better k...
Chrono methods (∆t > 1 ms)
Chrono methods (∆t > 1 ms) or Amperiometric Detection is a simple, widely used electrochemical measurement technique. At PalmSens it is better known under the name Chronoamper...
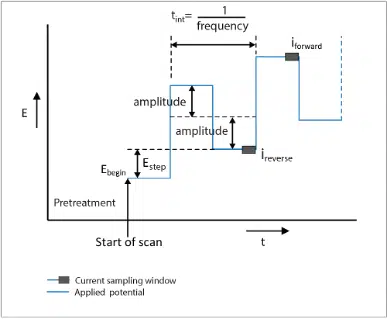
Square Wave Voltammetry (SWV)
Square Wave Voltammetry (SWW) is in fact a special version of Differential Pulse Voltammerty (DPV). Differential Pulse Voltammerty is Square Wave Voltammetry when t pulse is equal ...
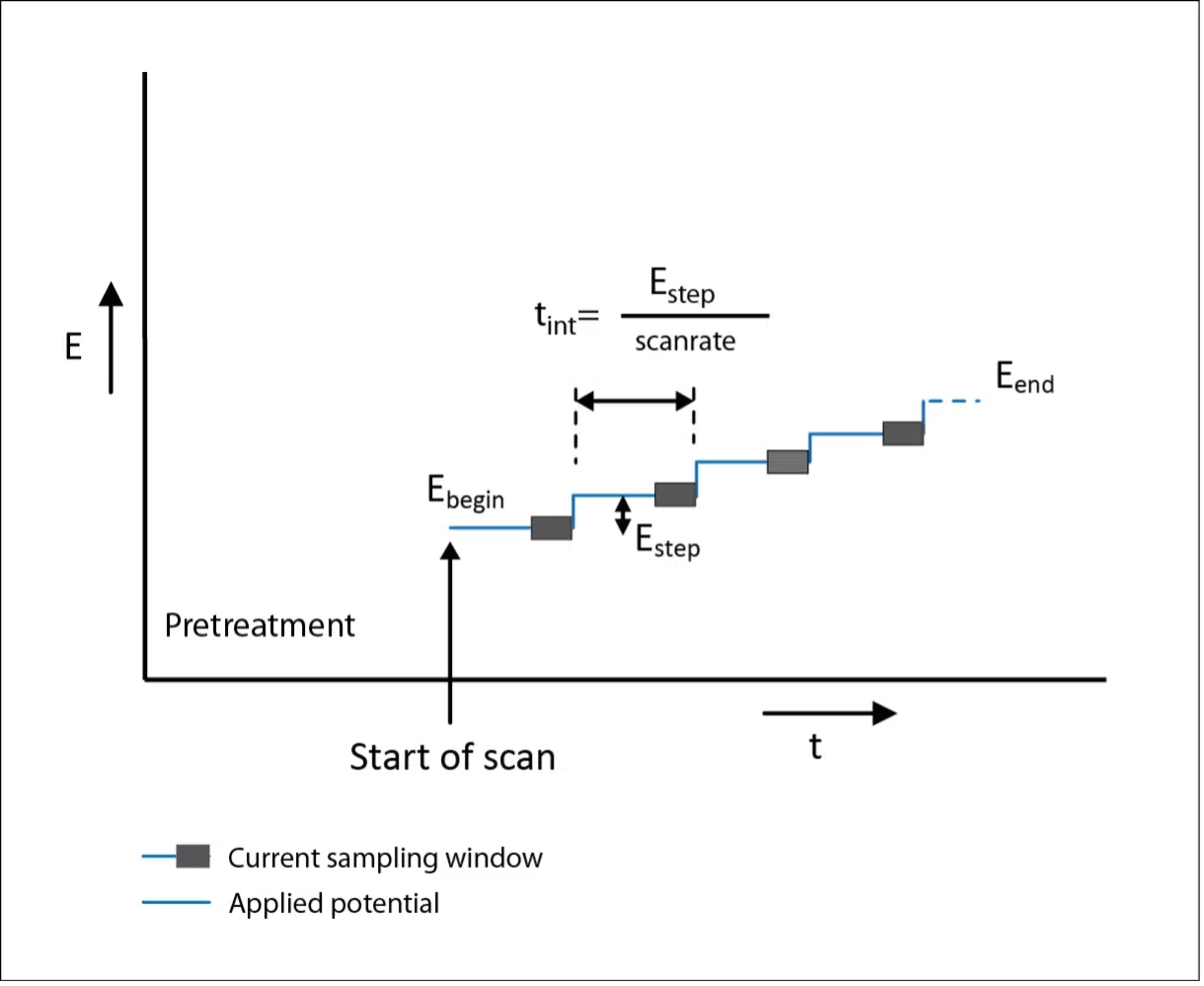
Linear Sweep Voltammetry (LSV)
Linear Sweep Voltammetry is also known as Linear Polarization. In Linear Sweep Voltammetry a potential scan is performed from the begin potential, E begin, to the end potential E e...
Time scan
Time scan is an electrochemical technique that can be applied with the following instruments from PalmSens: PalmSens4 EmStat4S Sensit Smart Sensit BT MultiPalmSens4 MultiEmStat4 ...
Potential scan or current scan
Potential scan or current scan is an electrochemical technique that can be applied with the following instruments from PalmSens: PalmSens4 EmStat4S MultiPalmSens4 ...
Mixed Mode (MM)
Mixed Mode (MM) is an electrochemical technique that can be applied with the following instruments from PalmSens: PalmSens4 EmStat4S MultiPalmSens4 ...
