Electrochemistry explained
Articles

What is noise, and how to avoid noise in electrochemistry?
Having noise in your electrochemical measurement? Looking for ways to reduce noise? This video is for you. Our electrochemist Lutz Stratmann will explain the concept of noise, and...

What are Screen-printed electrodes and which electrode should I choose?
Screen-printed electrodes make electrochemical detection very interesting for analysis in everyday life, especially point-of-care measurements. The measuring devices as well as el...
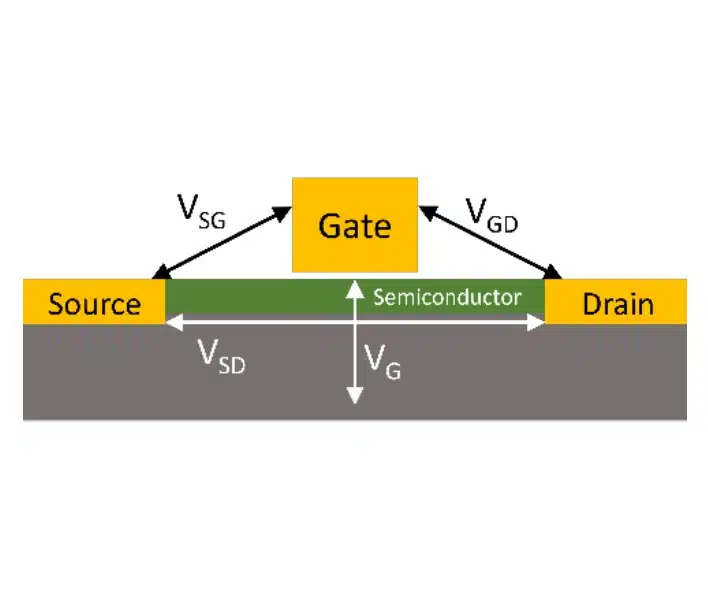
Electronic (bio)sensors using FET as the transducer
Part One is about FET fundamentals, different types of FETs, and how to use the EmStat Pico to characterize them. Part two is more focused on advanced FETs, for example, graphene...
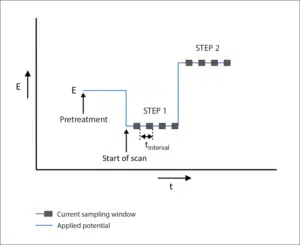
Coulometric Detection
Coulometric Detection is an electrochemical technique during which a potential is set. This technique is usually called Chronocoulometry at PalmSens. The current is recorded and shown in a graph versus the time.
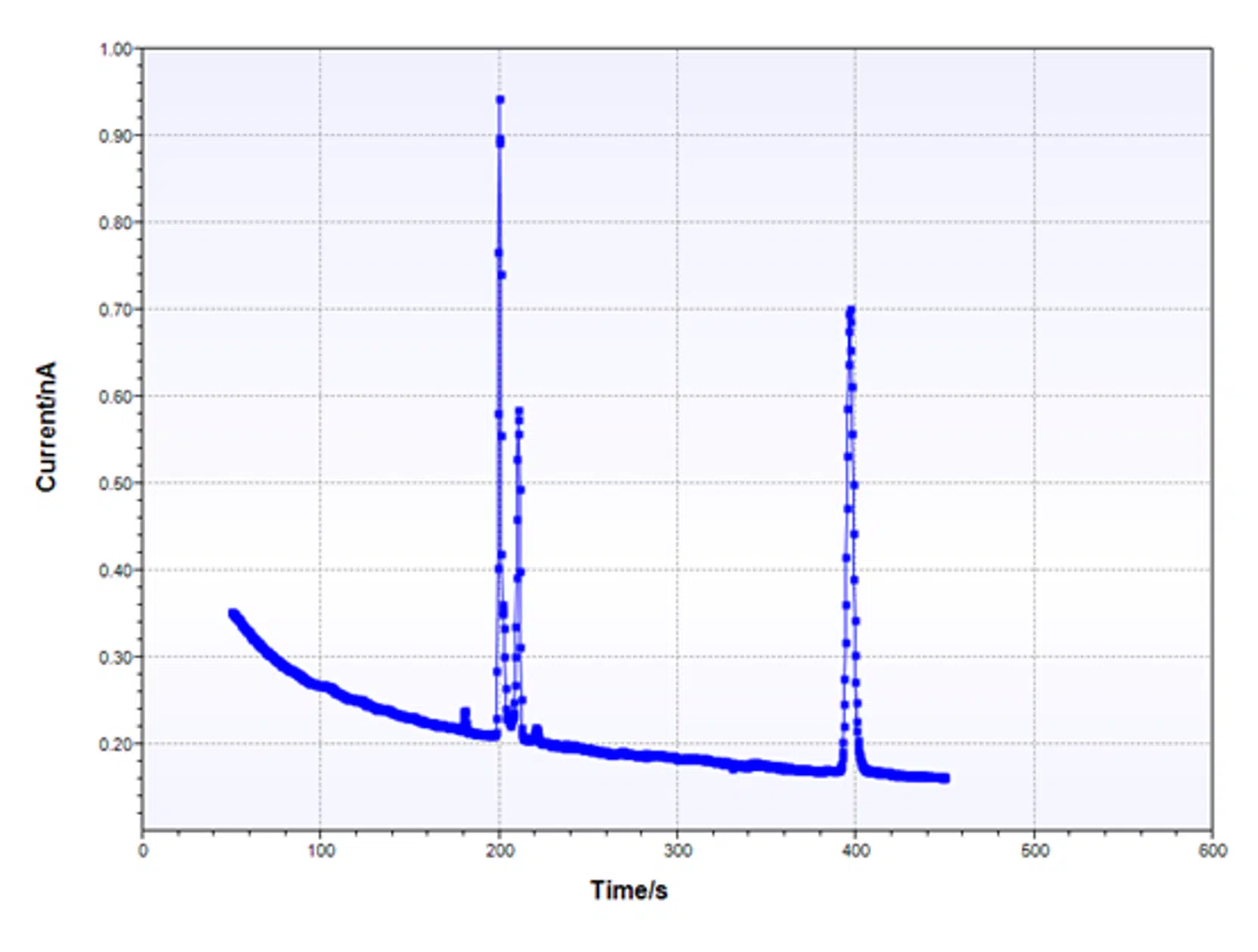
Potentiostatic Chronoamperometry
Potentiostatic Chronoamperometry is an electrochemical technique, usually called Chronoamperometry (CA) at PalmSens. Read all about it.

Constant Potential Chronoamperometry
Constant Potential Chronoamperometry is an electrochemical technique, usually called Chronoamperometry (CA) at PalmSens. Read all about it.

Potentiostatic DC Measurement
Potentiostatic DC Measurement is an electrochemical technique, usually called Chronoamperometry (CA) at PalmSens. Read all about it.

Amperometric i-t Curve (i-t)
An amperometric i-t Curve (i-t) is an electrochemical technique, usually called Chronoamperometry (CA) at PalmSens. Read all about it.

Potentiostatic Polarization
Potentiostatic Polarization is an electrochemical technique, usually called Chronoamperometry (CA) at PalmSens. Read all about it.
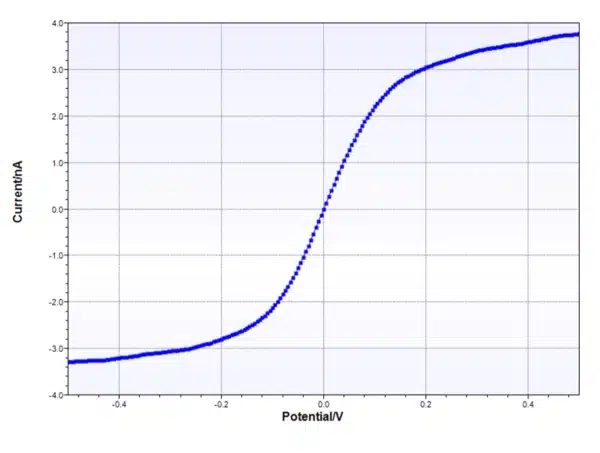
Reverse Normal Pulse Voltammetry
Reverse Normal Pulse Voltammetry is an electrochemical technique, usually called Normal Pulse Voltammetry at PalmSens. With Reverse Normal Pulse Voltammetry the influence of diffusion limitation on your I-E curve (Cottrel behavior) is removed.
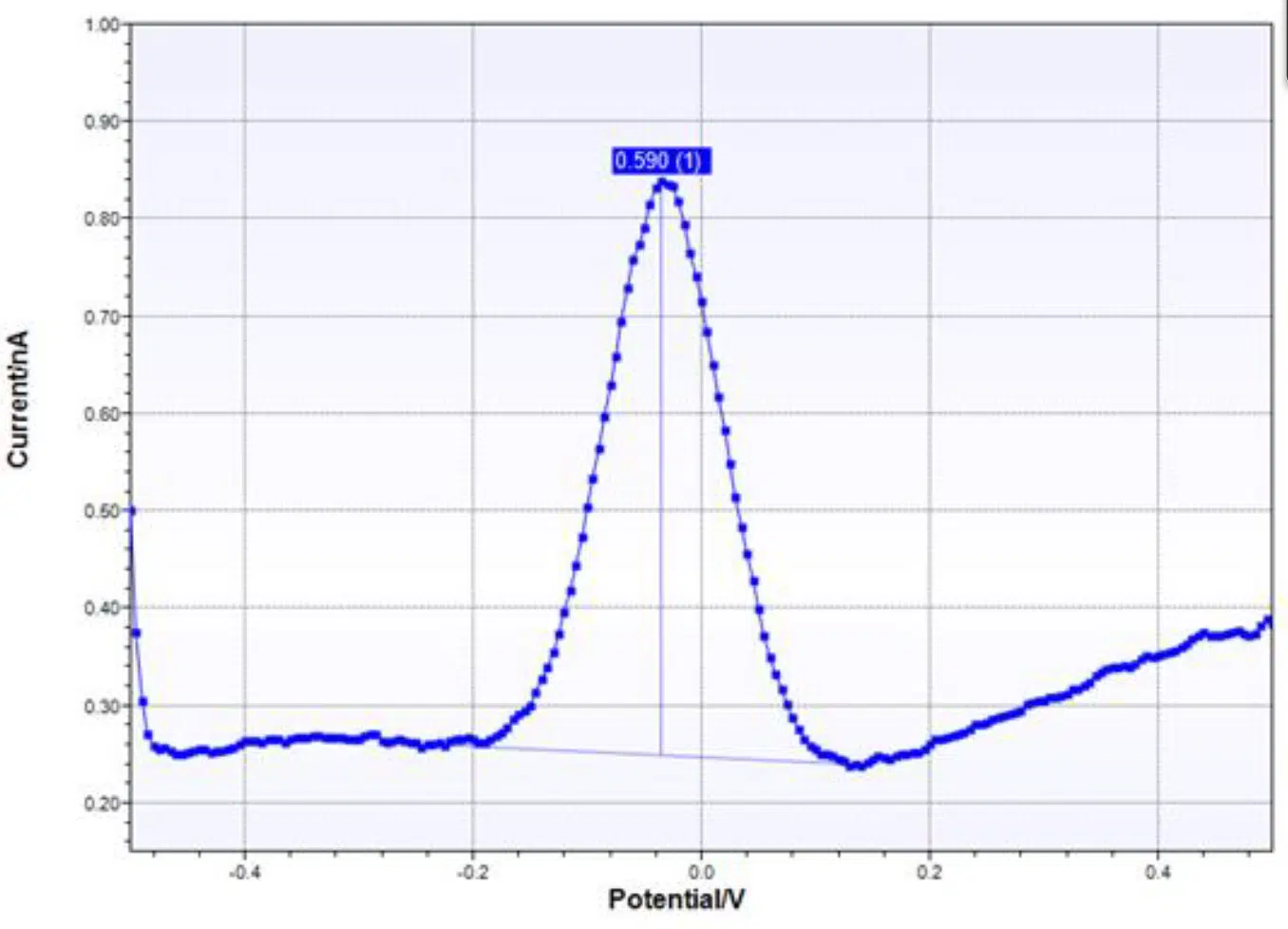
Pot. Differential Pulse
Pot. Differential Pulse is an electrochemical technique commonly called Differential Pulse Voltammetry at PalmSens.

Differential Pulse Polarography
Differential Pulse Polarography is an electrochemical technique commonly called Differential Pulse Voltammetry at PalmSens. ...
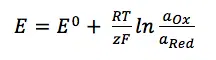
Nernst equation
The Nernst equation is one of the two central equations in electrochemistry. It describes the dependency of an electrode’s potential on its chemical environment.
Amperometric Detection
Amperiometric Detection or Chronoamperometry (CA) is a simple, widely used electrochemical measurement technique. Many sensors, like those for glucose or oxygen, require this technique.
Potentiometric stripping analysis
Potentiometric stripping analysis is a sensitive analytical technique. Before the SCP measurement starts a deposition stage at the deposition potential E dep is required. After th...
Chrono methods high speed (∆t > 100 ns)
Chrono methods high speed (∆t > 100 ns) is a form of amperometric detection with very high sampling rates or respectively very short interval times. At PalmSens is is better k...
Chrono methods (∆t > 1 ms)
Chrono methods (∆t > 1 ms) or Amperiometric Detection is a simple, widely used electrochemical measurement technique. At PalmSens it is better known under the name Chronoamper...

BiPotentiostat
A BiPotentiostat is a potentiostat with two working electrodes. One electrode is the counter electrode and the other is the reference electrode. The two working electrodes can be operated and monitored exactly simultaneously. A Bipotentiostat is sometimes called a BiPot.
