Biosensors
Articles

What are Screen-printed electrodes and which electrode should I choose?
Screen-printed electrodes make electrochemical detection very interesting for analysis in everyday life, especially point-of-care measurements. The measuring devices as well as el...

Demonstration of Caffeine Measurements
Caffeine is a widespread psychoactive substance. Most people consume it regularly in coffee, tea, energy drinks, cola, or similar beverages. It is also used in some medications to...

Demonstration of a ZP glucose biosensor with a PalmSens Sensit Smart
This webinar recording will show you a demonstration of a glucose biosensor designed by Z&P and powered by our Sensit Smart. The webinar consists of four parts: Introductio...
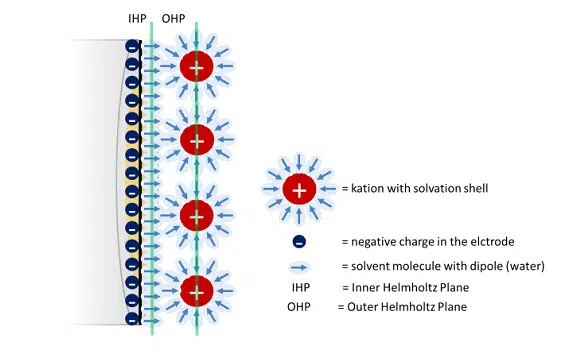
The Cottrell Experiment and Diffusion Limitation 3/3 – Electrochemical Double Layer
In this chapter the electrochemical double layer and its features are discussed. The electrochemical double layer acts as a capacitor and every change in the potential of the electrode will induce a capacitive charging current that is caused by physics not by a chemical reaction. This current decays exponentially.
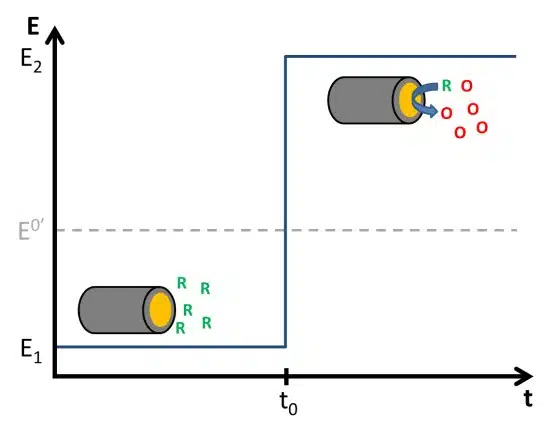
The Cottrell Experiment and Diffusion Limitation 2/3 – The Cottrell Experiment
In this chapter, we discuss the Cottrell experiment. During the Cottrell experiment a potential step across a redox potential is applied and the current caused by the electrochemical reaction is recorded. The current is controlled by diffusion.
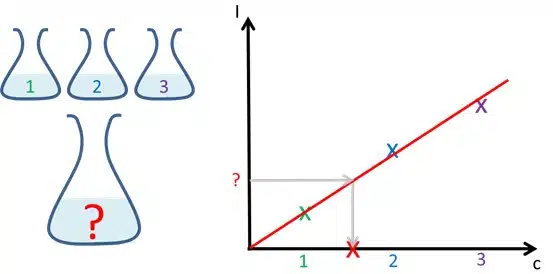
Detection of Hydrogen Peroxide 5/5 – The Calibration Curve
This chapter explains how to prepare and use a calibration curve.
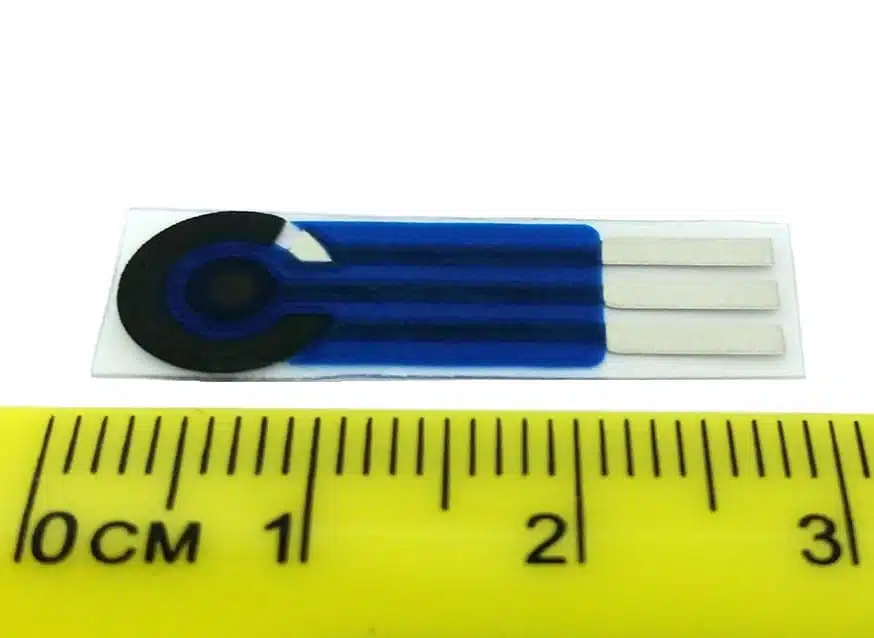

Detection of Hydrogen Peroxide 4/5 – with Prussian Blue
This chapter is part of the series ‘Detection of hydrogen peroxide with Prussian Blue’. This chapter delves deeper into the specifics of detecting hydrogen peroxide using Prussian Blue.

Detection of Hydrogen Peroxide 3/5 – What is Prussian Blue?
Prussian Blue (PB) is a deep blue pigment that is hardly soluble in water, but little amounts that are dissolved or dispersed in watercolor the solution intensively blue. Small Prussian Blue particles dispersed in water have been used as the first modern synthetic color. It is also known as Berlin Blue or Turnbull’s Blue. The pigment is used for various paints (Paris Blue) or to make the blue color for blueprints.

Detection of Hydrogen Peroxide 2/5 – Why detect Hydrogen Peroxide?
In this chapter, we explain what hydrogen peroxide is and why we detect it. Hydrogen peroxide is the simplest peroxide (a compound with an oxygen-oxygen single bond). It is also a strong oxidizer. Due to its oxidizing properties, hydrogen peroxide is often used as a bleach or cleaning agent.
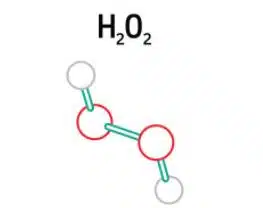
Detection of Hydrogen Peroxide 1/5 – Introduction
This series of articles aims to provide an introduction to electrochemical experiments. This series in particular deals with the detection of hydrogen peroxide with selfmade Prussian Blue electrodes, and includes an experiment (PDF) you can carry out yourself.

Detection of Glucose with a Self-Made Biosensor 5/5 – Glucose and Glucose Oxidase
This chapter is part of the series ‘Detection of glucose with a self-made biosensor based on glucose oxidase’. This chapter is the final theoretical part, which elaborates on the experiment with the enzyme Glucose Oxidase (GOx).
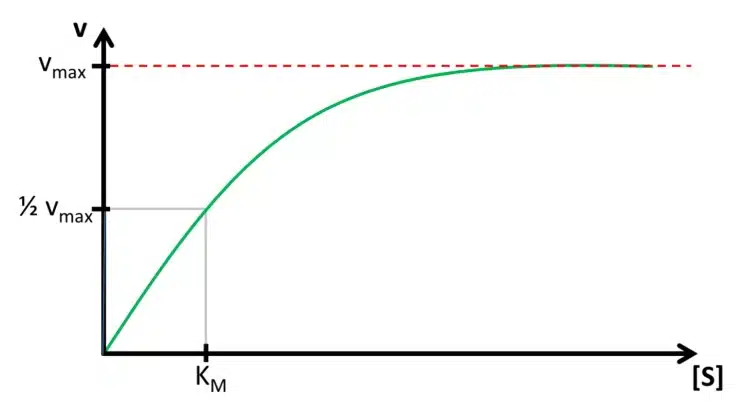
Detection of Glucose with a Self-Made Biosensor 4/5 – Michaelis-Menten Kinetics
In this chapter we discuss the theory of Michaelis-Menten and its importance for biosensors. The last section deals with the Lineweaver-Burk plot.
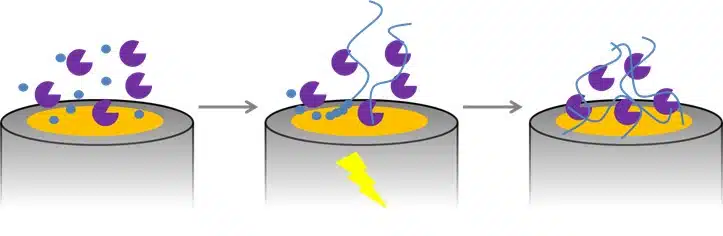
Detection of Glucose with a Self-Made Biosensor 3/5 – Immobilization of Enzymatic Biosensors
In this section, we elaborate on the workings of biosensors. More specifically, the immobalization thereof.

Detection of Glucose with a Self-Made Biosensor 1/5 – Introduction
This series of articles aims to provide an introduction to electrochemical experiments. This series in particular deals with the detection of glucose with a self-made biosensor based on glucose oxidase, and includes an experiment (PDF) you can carry out yourself.
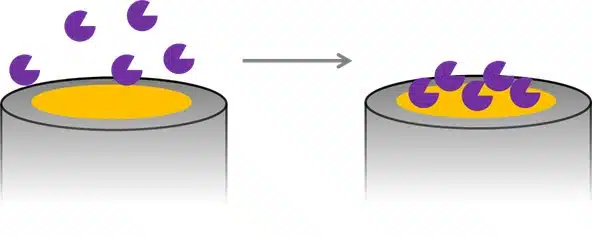
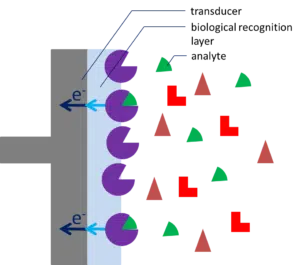
Detection of Glucose with a Self-Made Biosensor 2/5 – What is a Biosensor?
This chapter is part of the series ‘Detection of glucose with a self-made biosensor based on glucose oxidase’. This section provides a basic introduction to biosensors....
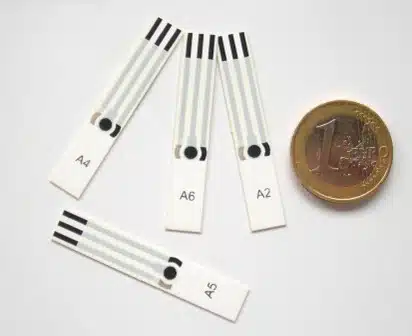
Screen Printed and Film Electrodes
Screen printed and film electrodes are suitable for mass production, versatile, cheap, and easy to handle. They make electrochemistry available to users without electrochemical knowledge.

Future of electrochemical sensors
Curious how electrochemical sensors will be used in the future? Niels van Velzen, the CTO of PalmSens, explains about biosensor strips and portable readers. The readers perform mea...
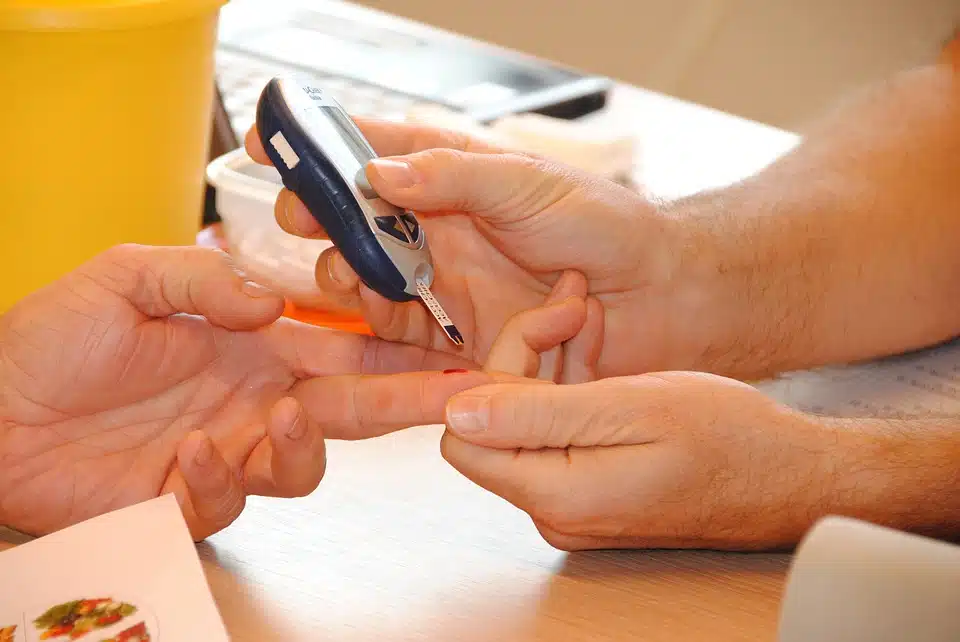
Biosensor
A biosensor is a sensor exploiting a biomolecule and is used to measure the presence of a certain substance in a liquid. For example, the medical world uses biosensors to detect a virus in the blood or to measure glucose levels in blood. These are mainly point-of-care applications, where direct results are important.
