Corrosion current
Current is the movement of charge per time and usually electrons are the charge carriers. The corrosion current is the current flowing inside a corroding system and thus it is the current responsible for the corrosion.
For example, if an iron surface is corroding due to an oxidation by oxygen and the oxygen is reduced to hydroxide, the electrons flowing from the iron to the oxygen are the corrosion current.
With the corrosion current the corrosion rate can be determined. The corrosion current can be extracted from a polarization curve via a Tafel analysis. All these terms are described in more detail in the corresponding articles.
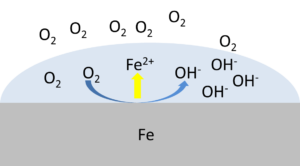
Articles
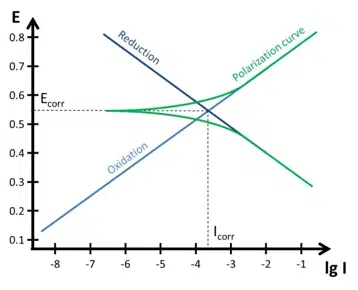
Tafel Plot and Evans Diagram
To understand the foundation of corrosion current measurements the Tafel plot and the Evan’s diagram are explained. The connection between a polarization curve and the Evan’s diagram is explained and how to extract the corrosion current from a polarization curve.
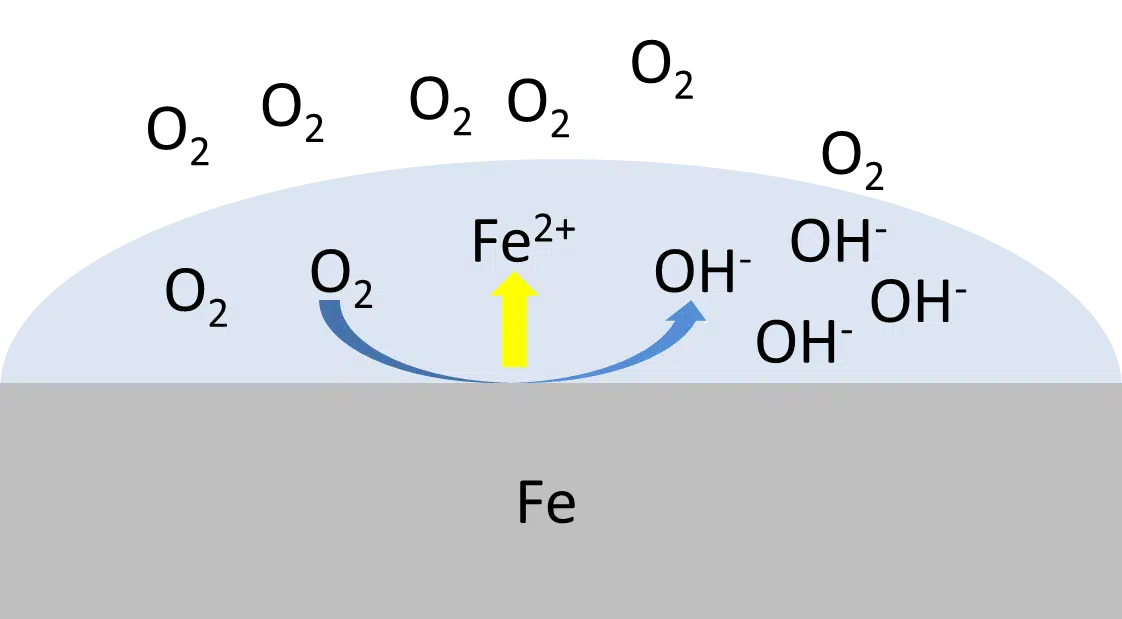
Corrosion current
In this article the corrosion current, a fundamental parameter in corrosion research, is introduced.
