Corrosion
Wikipedia says that “Corrosion is a natural process that converts a refined metal into a more chemically stable form such as oxide, hydroxide, carbonate or sulfide. It is the gradual destruction of materials (usually a metal) by chemical and/or electrochemical reaction with their environment. Corrosion engineering is the field dedicated to controlling and preventing corrosion.” (https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Corrosion, status 2021-05-18)
Many corrosion processes, especially metal corrosion, is caused by electrochemical reactions. The oxidizer is in many cases oxygen. Most metal objects are exposed to the air, which contains oxygen, and thus might corrode.
Corrosion researchers try to understand the reasons for corrosion down to the atomic scale with the goal to develop new methods of effective corrosion protection.
Electrochemical methods are perfect to studies the different properties of a system, which influence the corrosion processes. Electrochemistry provides within a short time period. Feel free to browse the knowledge base to learn about the possibilities.
Articles

Introduction to the Corrosion Research Knowledgebase
This knowledgebase contains all you need to understand potentiostats, electrodes and how to use them to perform for example coating research or analyze paint. It will give an intro...

Copper and Nickel Deposition 2/3 – Corrosion research and corrosion protection
This chapter explains corrosion and methods to prevent it. Corrosion is an important research field due to the fact that corrosion causes big amounts of damage to machines and monuments. Understanding and preventing corrosion is the goal of corrosion research.

List of symbols for corrosion research
Here you will find all the symbols used by us in this knowledge base. Please note that other publications might use different symbols for the same parameters.
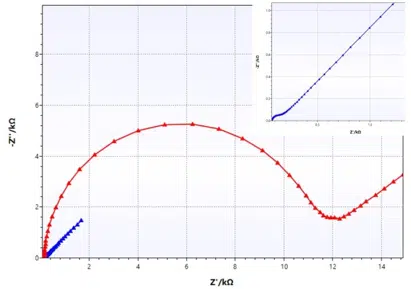
Equivalent circuit fitting for corrosion measurements
In this section of the handbook the Warburg Impedance and the Constant Phase Element (CPE) are introduced, which represent electrochemical effects with no corresponding real electronic components. Furthermore, some equivalent circuits for typical corrosion systems are presented.
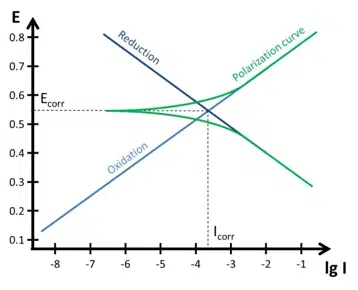
Tafel Plot and Evans Diagram
To understand the foundation of corrosion current measurements the Tafel plot and the Evan’s diagram are explained. The connection between a polarization curve and the Evan’s diagram is explained and how to extract the corrosion current from a polarization curve.
Corrosion current
In this article the corrosion current, a fundamental parameter in corrosion research, is introduced.

Corrosion Potential
In this chapter the Open Circuit Potential (OCP) and the Corrosion Potential are introduced. The principles of reference electrodes as well as the 0 V by convention potential of the standard hydrogen electrode (SHE) are explained.
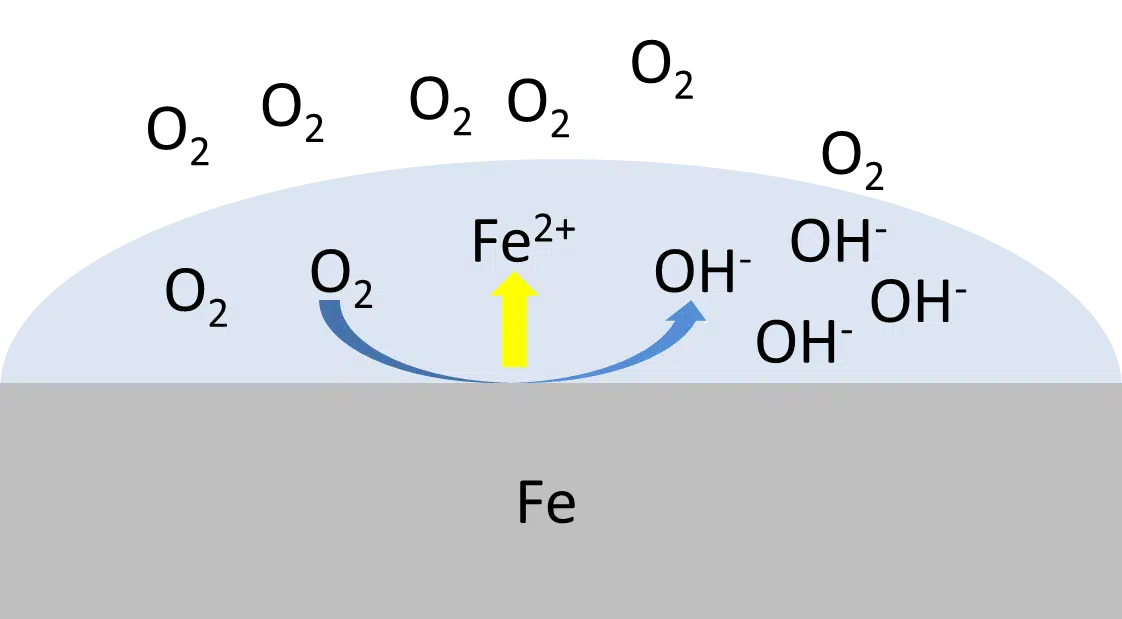
Origins of electrochemical potentials
This section is a short explanation of the processes that lead to electrochemical potential and thus to corrosion processes.
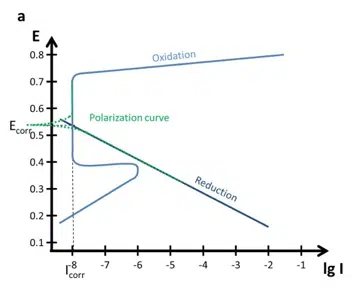
Polarization Curves: setup, recording, processing and features
In this extensive section Polarization Curves are discussed. How to setup your equipment, the choice of parameters as well as the data processing is discussed. This will enable you to record a polarization curve and extract the corrosion rate from it by using PSTrace 5. Furthermore, the polarization curves and Evan’s diagrams for passivation films (thick and thin) are discussed. This section closes with a brief description of crevice and pitting corrosion.
