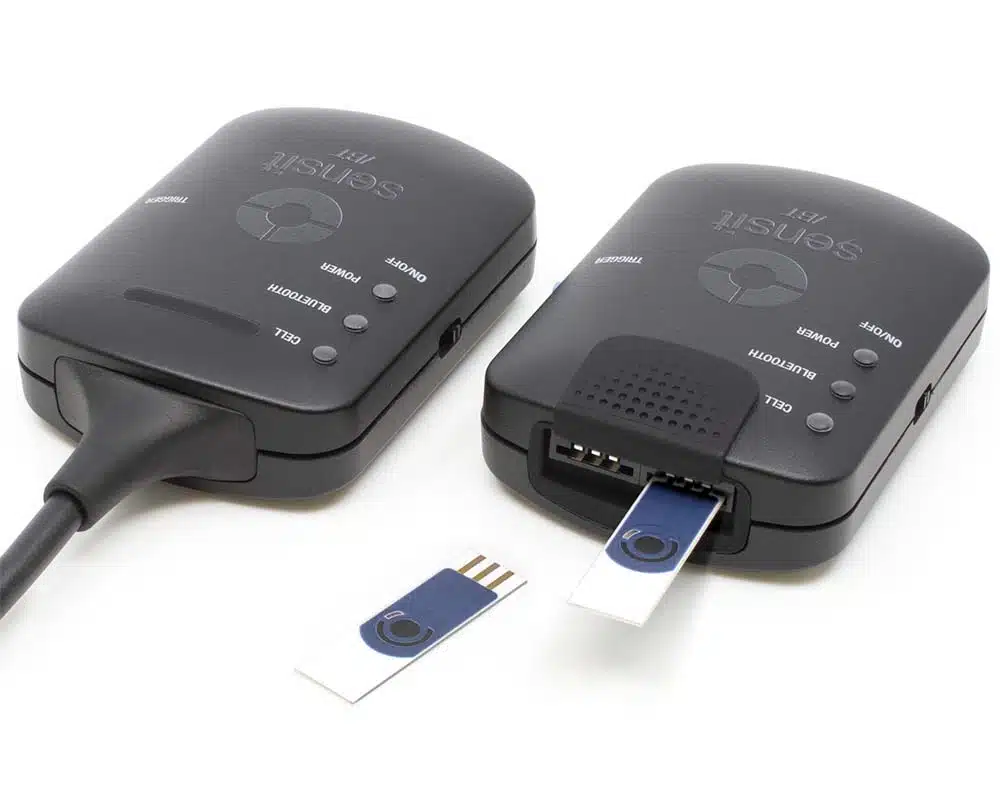
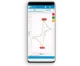
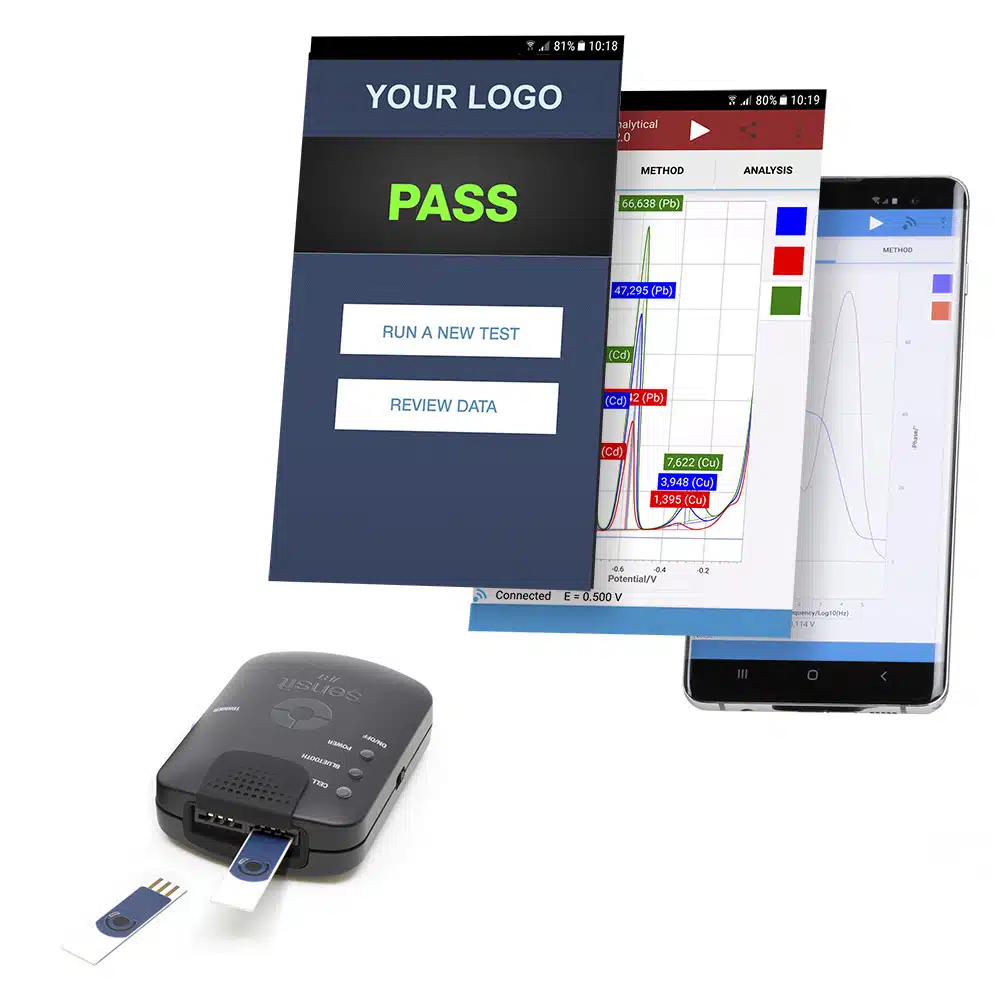
Sensit BT for OEM
Tailored for your application
- Capable of EIS up to 200 kHz
- Battery & Wireless communication integrated
- Customization (e.g. logo and color) possible, even for small series
- Easy app building using our tools and examples
- Can be used without PC or smartphone connection
Description

The Sensit BT connects wirelessly to your smartphone or tablet and controlled via the Android app PStouch. You can use the USB-C port to charge the Sensit BT or connect to a classic USB port on your PC and control the Sensit BT via our PC software PSTrace.
The Sensit BT supports most common electrochemical techniques, including Cyclic Voltammetry, Square Wave Voltammetry and Impedance Spectroscopy (FRA/EIS).
Two versions:
|
Sensit BT.SPE |
Sensit BT.SNS |
||
|
|
|
||
| Sensor pitch | 2.54 mm | Cable length | 40 cm |
| Electrode connections | RE, WE, CE / Custom | Connectors | 2 mm banana |
| Allowed sensor thickness | Between 0.1 mm and 0.8 mm | Electrode connections | RE, WE, WE2, CE |
| Maximum sensor width | 11 mm | ||
Dual-channel and Bipotentiostat
The Sensit BT.SPE can be used for running sequential measurements on two different Screen-Printed Electrodes (SPE’s) each with their own Reference, Counter and Working electrodes.
The second channel can also be used in Bipotentiostat mode, functioning as second Working Electrode versus the Reference and Counter electrode of channel 1. Both working electrodes are recorded simultaneously in the Bipotentiostat mode.
The Sensit BT.SNS has a lead connected to the WE of channel 2 and can be used out-of-the-box for BiPotentiostat measurements.
On-board data storage

Save measurements on-board as a backup. Or pre-program the device with a script and use the trigger button to run and store measurements: no need to connect a PC or smartphone. Browse and transfer all internally stored measurements back to the PC easily using PSTrace for Windows.
Specifications
- Dual-Channel potentiostat with bipotentiostat mode
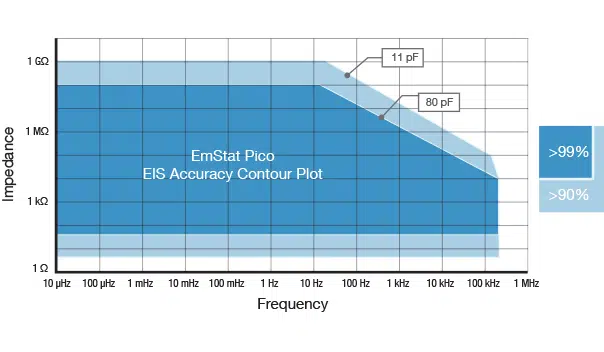
- FRA / EIS up to 200 kHz
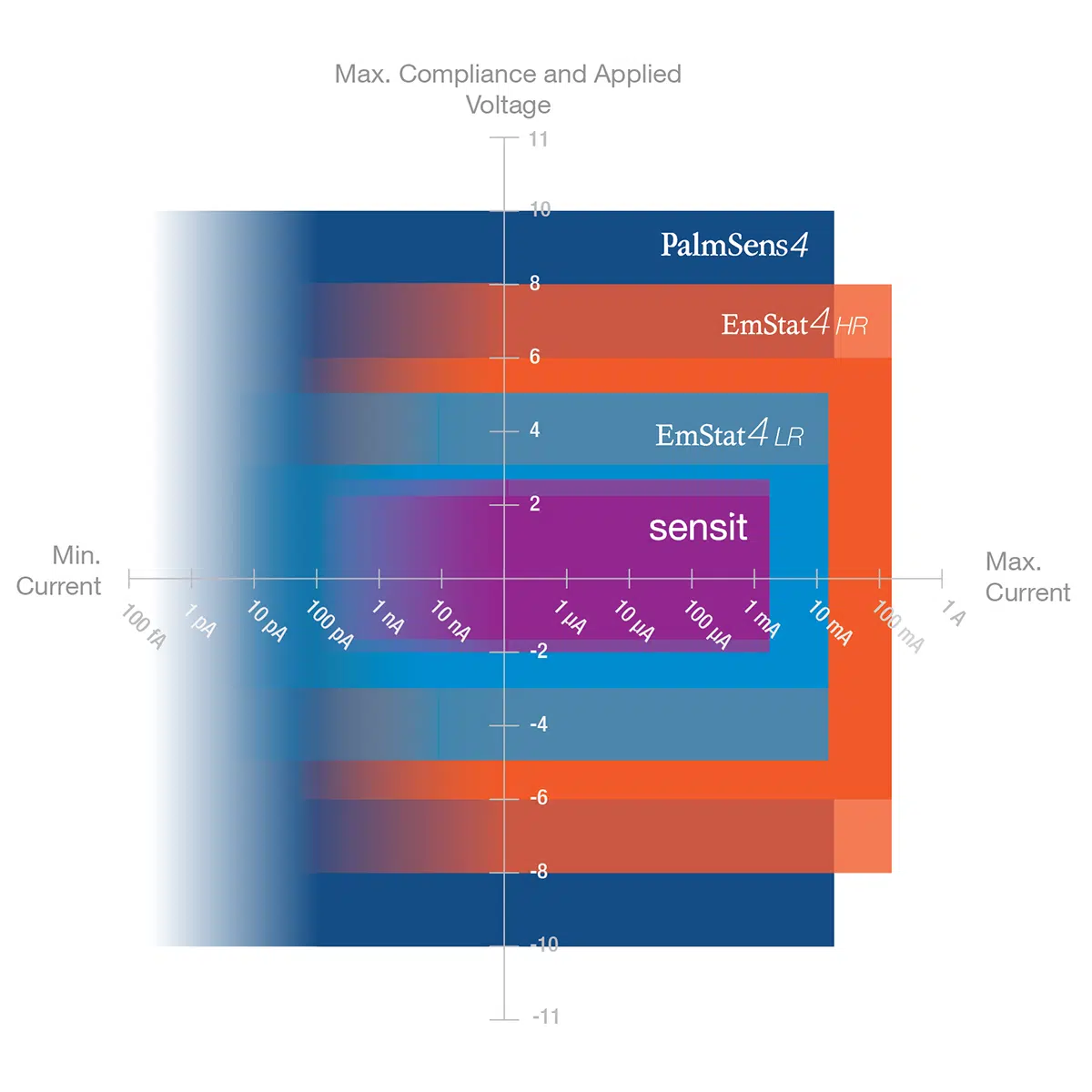
- Potential range -1.7 to +2 V
- Current ranges 100 nA – 5 mA (max ±3 mA)
See EmStat Pico module for more detailed specifications.
| Other | |
|---|---|
| Power | USB / battery |
| Communication | USB (type C) and Wireless communication (Classic and BLE) |
| Dimensions | 75 x 55 x 23 mm (excl. cable) |
| Weight | 75 g |
| Battery life | 12 hours at max. power consumption Full charge in < 3 hours |
| Auxiliary port | No |
| Storage memory | 500 MB for storing up to 16 million datapoints |
EIS Accuracy Contour Plot
Software Development
Develop software for PC and smartphone
Whether you want to write a simple or advanced Windows application, develop an Android or iPhone app you can do it with our software development tools and code examples.
The Sensit BT and Sensit Smart can also be controlled directly with our PSTrace software for Windows and PStouch app for Android.

Software Development Kits for .NET
The PalmSens Software Development Kits (SDKs) for .NET can be used with any of our instruments or OEM potentiostat modules to develop your own software. The SDK’s come with a set of examples that shows how to use the libraries.
PalmSens SDKs with examples are available for the following .NET Frameworks:
- WinForms
- WPF
- Xamarin (for Android)
- UWP
MethodSCRIPT™ communications protocol
The Sensit Series have an on-board parser for the MethodSCRIPT™ scripting language. This language allows developers to program a human-readable script for the Sensit Series on any platform or operating system. The simple script language allows for running electrochemical techniques supported by the Sensit Series and makes it easy to combine different measurements and other tasks.

Compatibility
My sensor fits the connector.
The required electrochemical technique for my application is supported.
The analyte conductivity does not require a compliance voltage of 2/2.3 V.
Downloads
Software (9)
| Name | Last updated | |
|---|---|---|
| PSTrace PC software for all single channel instruments PSTrace software is shipped as standard with all single channel and multiplexed instruments. The software provides support for all techniques and device functionalities. | 08-07-24 | |
|
MethodSCRIPT code examples
MethodSCRIPT code examples include:
- MethodSCRIPTExample_C - MethodSCRIPTExample_C_Linux - MethodSCRIPTExample_C# - MethodSCRIPTExample_Arduino - MethodSCRIPTExample_Python - MethodSCRIPTExample_iOS - MethodSCRIPTExample_Android Every code example comes with a "Getting Started" document. |
07-07-24 | |
| PS Laird BT900 Upgrade Tool Use this tool to update your OEM device for use with Dual Mode wireless communication settings (SPP and BLE). Works with EmStat Pico Dev Board, Sensit BT and EmStat Go. | 21-11-22 | |
| PSExampleApp: Configurable and Open-Source App for Sensor Applications The PSExampleApp is a simple open-source application that guides a user to do a measurement with a PalmSens device to measure concentrations in a liquid sample. The app can be re-configured without code for use with (bio)sensors measuring a specific analyte using a linear calibration curve.. This file contains the example configuration files to customize the app and links to both the Android and iOS version of the app. | 21-07-22 | |
| EmStat Pico Firmware v1.3.4 See app note "EmStat Pico firmware updating" for more information about updating built-in and bare EmStat Pico modules. | 13-12-21 | |
| EmStat Pico Firmware v1.2 See app note "EmStat Pico firmware updating" for more information about updating built-in and bare EmStat Pico modules. | 13-12-21 | |
| Getting started with PalmSens SDK for WPF This manual explains how to use the SDK with the included libraries and examples. | 07-06-21 | |
| Getting started with PalmSens SDK for WinForms This manual explains how to use the SDK with the included libraries and examples. | 07-06-21 | |
| Getting started with PalmSens SDK for Android This manual explains how to use the SDK with the included libraries and examples. | 07-06-21 |
Documentation (7)
| Name | Last updated | |
|---|---|---|
| MethodSCRIPT v1.5 The MethodSCRIPT scripting language is designed to improve the flexibility of the PalmSens potentiostat and galvanostat devices for OEM users. It allows users to start measurements with arguments that are similar to the arguments in PSTrace. PalmSens provides libraries and examples for handling low level communication and generating scripts for MethodSCRIPT devices such as the EmStat Pico and EmStat4. | 25-03-24 | |
| MethodSCRIPT v1.4 The MethodSCRIPT scripting language is designed to improve the flexibility of the PalmSens potentiostat and galvanostat devices for OEM users. It allows users to start measurements with arguments that are similar to the arguments in PSTrace. PalmSens provides libraries and examples for handling low level communication and generating scripts for MethodSCRIPT devices such as the EmStat Pico and EmStat4. | 01-02-23 | |
| Sensit BT Brochure Sensit BT Brochure | 09-09-22 | |
| EmStat Pico communication protocol v1.3 This document describes the “online” communication protocol of the EmStat Pico. Initial communication with an EmStat Pico is always done using this online communication. Measurements and other scripts can be started by sending a MethodSCRIPT, | 13-06-22 | |
| MethodSCRIPT v1.2 MethodSCRIPT v1.2 protocol description | 28-04-20 | |
| MethodSCRIPT v1.1 MethodSCRIPT v1.1 protocol description | 17-04-20 | |
| EmStat Pico communication protocol v1.2 Describes the EmStat Pico communications protocol which is based on MethodSCRIPT | 08-04-20 |
Application Note (4)
| Name | Last updated | |
|---|---|---|
| Changing Wireless Communication Settings for OEM This tutorial describes how to change the settings of the LAIRD BT900 Wireless communication module on PalmSens devices for OEM. | 14-10-21 | |
| Vitamin C Detection with ItalSens IS-C This application note describes how to create a calibration for quantitative measurements of vitamin C. Due to the detailed description and harmless solutions this an excellent electrochemical experiment with liquids for beginners in the field of electrochemistry. | 27-01-21 | |
| Limitations for EIS on EmStat Pico | 18-12-20 | |
| Connect SensitBT using wireless communication This application note describes various ways to connect the portable SensitBT using wireless communication. To connect using Android you can use PSTouch, in Windows you can use PSTrace or MethodSCRIPT. In iOS you can use MethodSCRIPT. | 10-11-20 |