BiPotentiostat
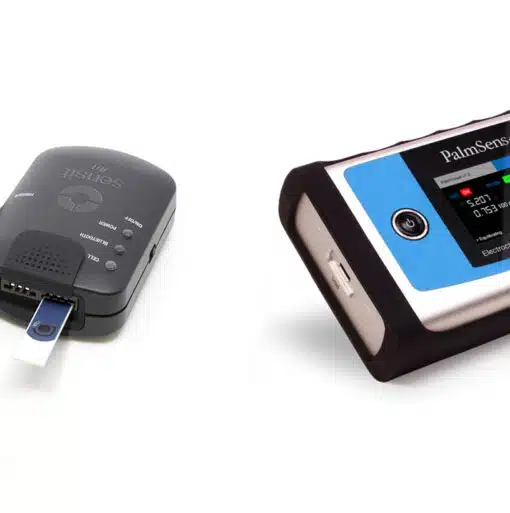
A BiPotentiostat is a potentiostat with two working electrodes, one counter electrode, and one reference electrode. The two working electrodes can be operated and monitored exactly simultaneously.
A regular potentiostat, or monopotentiostat to emphasize that it is just one working electrode, has three types of electrodes:
- Reference electrode: This electrode has a constant OCP (Open Circuit Potential) and is the reference point of the potentiostat.
- Working electrode: This is the electrode where the reaction of interest occurs.
- Counter or auxiliary electrode: This is the electrode that completes the circuit with the working electrode, so a current can flow.
The difference between a normal potentiostat and a BiPotentiostat is the number of working electrodes. A normal potentiostat has one working electrode, while a BiPotentistat has two. The capabilities of the BiPot, which is short for BiPotentiostat, differ per instrument.
What do the working electrodes do in a BiPotentiostat?
Working electrode 1 performs one of the techniques listed at the bottom of this page while working electrode 2 can have its own constant potential or follow the potential of working electrode 1. In the latter case, you can have a potential offset between working electrodes 1 and 2 keeping the potential difference between both electrodes constant.
Application examples:
- Second electrode as blank or similar in the same cell for comparison
- Detection of the reaction product of the disc electrode at the ring of a RRDE (Rotating
- Ring Disc Electrode)
- Polarization of the surface during scanning electrochemical microscopy (SECM)
- Control of a transistor’s gate voltage (ISFET)
What electrochemical techniques can be performed with a BiPotentiostat?
In BiPotentiostat mode, the Sensit BT and the PalmSens 4 supports the following techniques:
- Linear Sweep Voltammetry (LSV)
- Cyclic Voltammetry (CV)
- Chronoamperometry (CA)
- Chronocoulometry (CC)
- Multistep Amperometry (MA)
What PalmSens instruments have a BiPotentiostat?
The Sensit BT.SNS comes with BiPot channel. The PalmSens4 is available with BiPot module for all PalmSens4 configurations. The BiPot module can be controlled with PSTrace for Windows and PStouch for Android.
| BiPot specifications PalmSens4 | |
|---|---|
| dc-potential range | ±5 V |
| dc-potential resolution | 153 µV |
| dc-offset error | ≤ 0.1% ±1 mV offset |
| accuracy | ≤ 0.1% |
| current ranges | 100 pA to 10 mA (9 ranges) |
| maximum measured current | i(WE1) + i(WE2) < 30 mA |
| current resolution | 0.005% of current range (5 fA on 100 pA range) 0.0025% of 10mA range |
| current accuracy | ≤ 0.1% at Full Scale Range all with additional 0.2% offset error |
| connection | Comes with a sensor cable with an additional (yellow) connector for WE2 |
| power | Comes with additional USB Y-cable for extra power |
| BiPot specifications Sensit BT.SNS | |
|---|---|
| Full dc-potential range | -1.2 to +2 V |
| Dynamic dc-potential range [1] | 2.2 V |
| Compliance voltage | -2.0 to +2.3 V [2] |
| Maximum current | ± 3 mA |
| Max. data acquisition rate | 400k |
| Supports FRA/EIS | Yes |
[1] The dynamic range is the range that can be covered during a single scan within the full potential range. For example; a linear scan can start at -1.5 V and end at 1.1 V or vice versa, covering 2.6 V dynamic range.
[2] The compliance voltage is the maximum potential between Working and Counter electrode and depends on the selected mode.
Related articles

(Bi)Potentiostat
What is a potentiostat and what is it used for? A short and simple explanation.
Read article
BiPotentiostat
What is the difference between a potentiostat and a bipotentiostat? Why use it?
Read article
Multi-channel potentiostat
A device made for multiple experiments which run parallel at the same time. Read all about it.
Read article
Economical potentiostat
If you want to do electrochemical measurements with a specific purpose in mind, you may need an economically priced potentiostat.
Read article
Portable potentiostat
An electrochemical measurement instrument used to carry out measurements in the field and have results available immediately.
Read articleDefinition of a BiPotentiostat
- BiPotentiostat
- A BiPotentiostat is a potentiostat with two working electrodes, one counter electrode, and one reference electrode.
Frequently Asked Questions about BiPotentiostats
What is a BiPotentiostat?
A BiPotentiostat is a potentiostat with two working electrodes, one counter electrode, and one reference electrode. The two working electrodes can be operated and monitored exactly simultaneously.
A regular potentiostat, or monopotentiostat to emphasize that it is just one working electrode, has three types of electrodes:
- Reference electrode: This electrode has a constant OCP (Open Circuit Potential) and is the reference point of the potentiostat.
- Working electrode: This is the electrode where the reaction of interest occurs.
- Counter or auxiliary electrode: This is the electrode that completes the circuit with the working electrode, so a current can flow.
The difference between a normal potentiostat and a BiPotentiostat is the number of working electrodes. A normal potentiostat has one working electrode, while a BiPotentistat has two. The capabilities of the BiPot, which is short for BiPotentiostat, channel differ per instrument.
What electrochemical techniques can be performed with a BiPotentiostat?
In BiPotentiostat mode, the PalmSens 4 supports the following four techniques:
- Linear Sweep Voltammetry (LSV)
- Cyclic Voltammetry (CV)
- Chronoamperometry (CA)
- Chronocoulometry (CC)
- Multistep Amperometry (MA)
The Sensit BT supports in BiPotentiostat-mode the following techniques:
What PalmSens instruments have a BiPotentiostat?
What do the working electrodes do in a BiPotentiostat?
Working electrode 1 performs one of the techniques listed at the bottom of this page while working electrode 2 can have its own constant potential or follow the potential of working electrode 1. In the latter case, you can have a potential offset between working electrodes 1 and 2 keeping the potential difference between both electrodes constant.
Why use a BiPotentiostat?
- Second electrode as blank or similar in the same cell for comparison
- Detection of the reaction product of the disc electrode at the ring of a RRDE (Rotating
- Ring Disc Electrode)
- Polarization of the surface during scanning electrochemical microscopy (SECM)
- Control of a transistor’s gate voltage (ISFET)