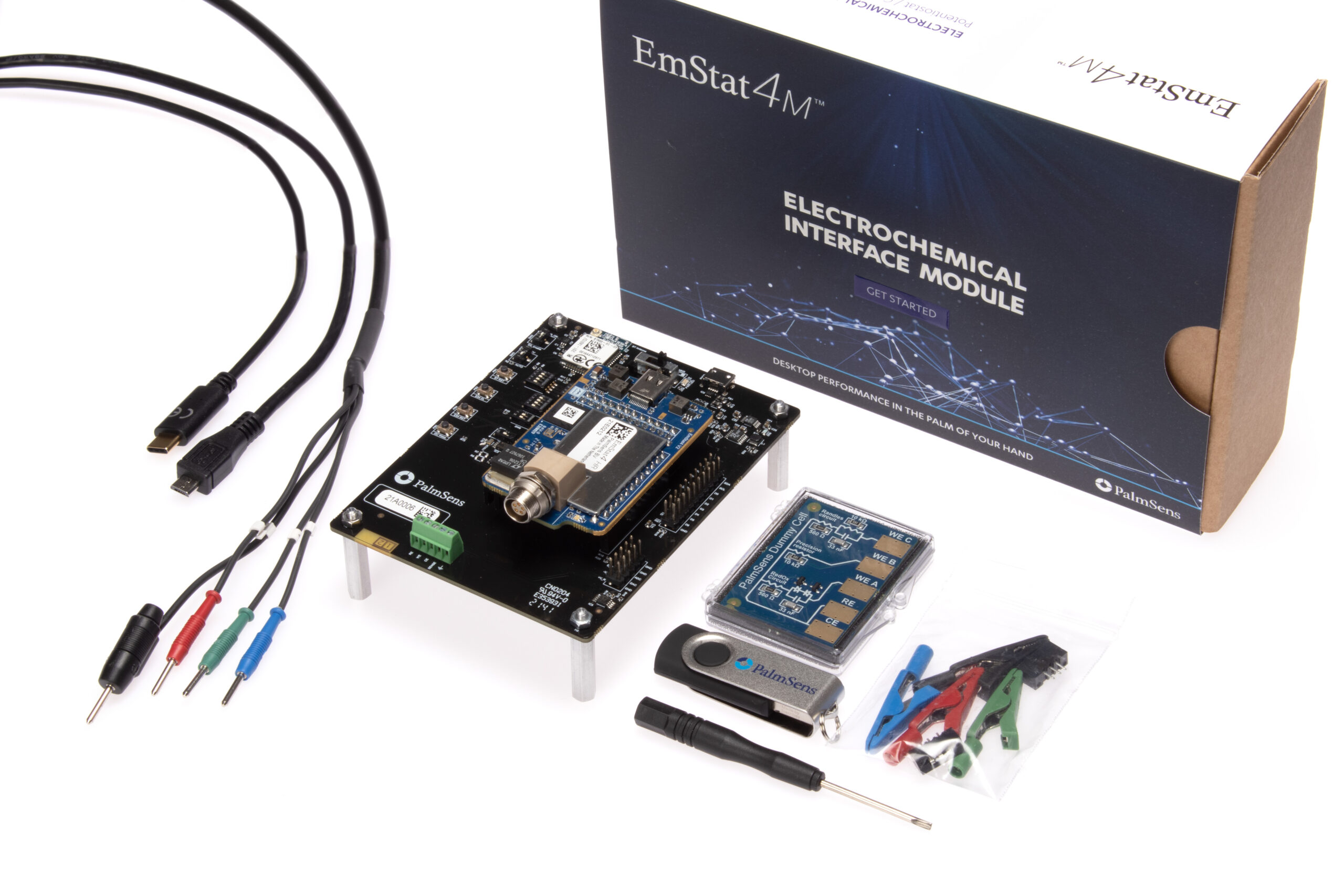
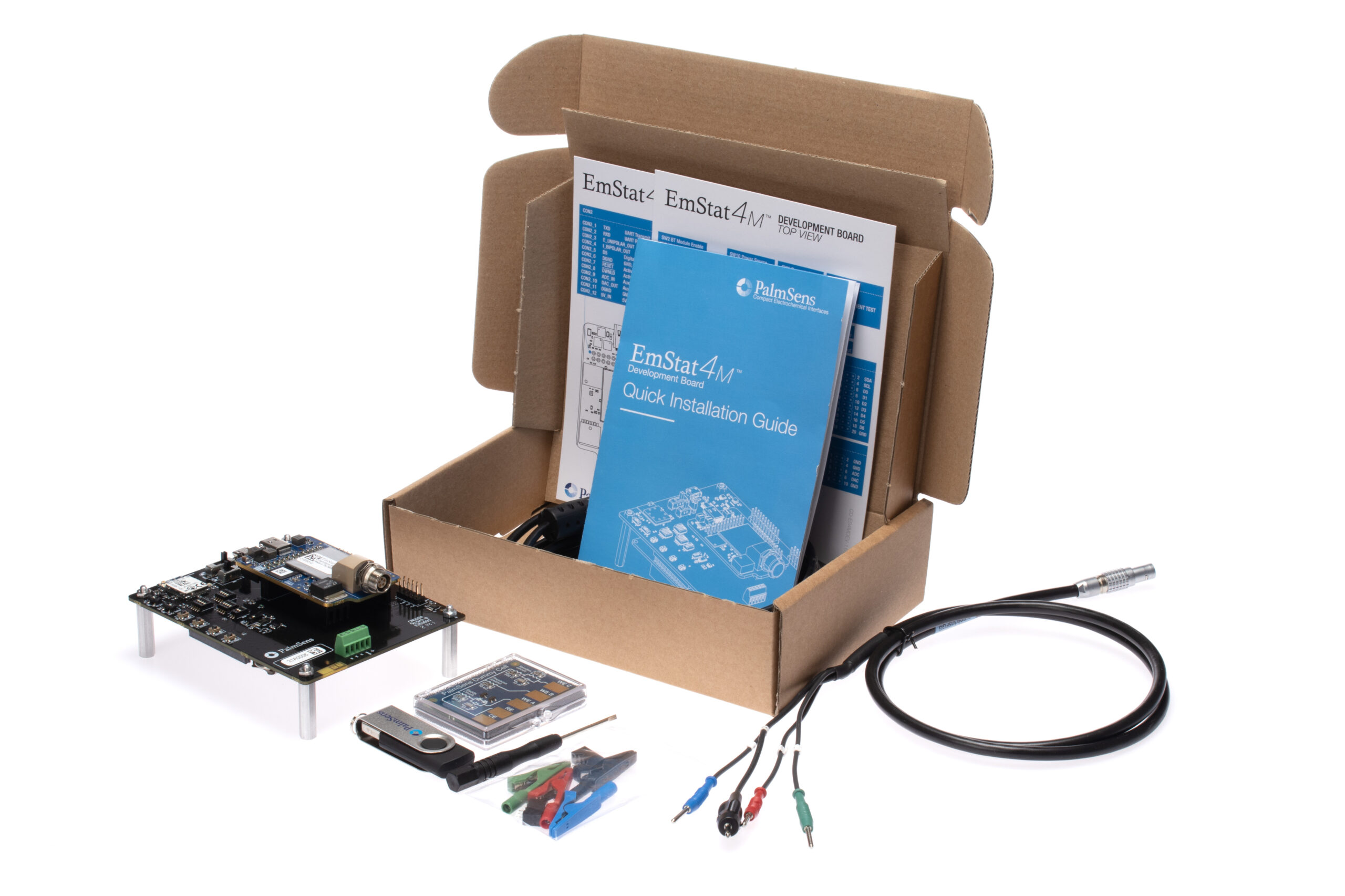
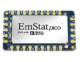
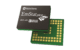
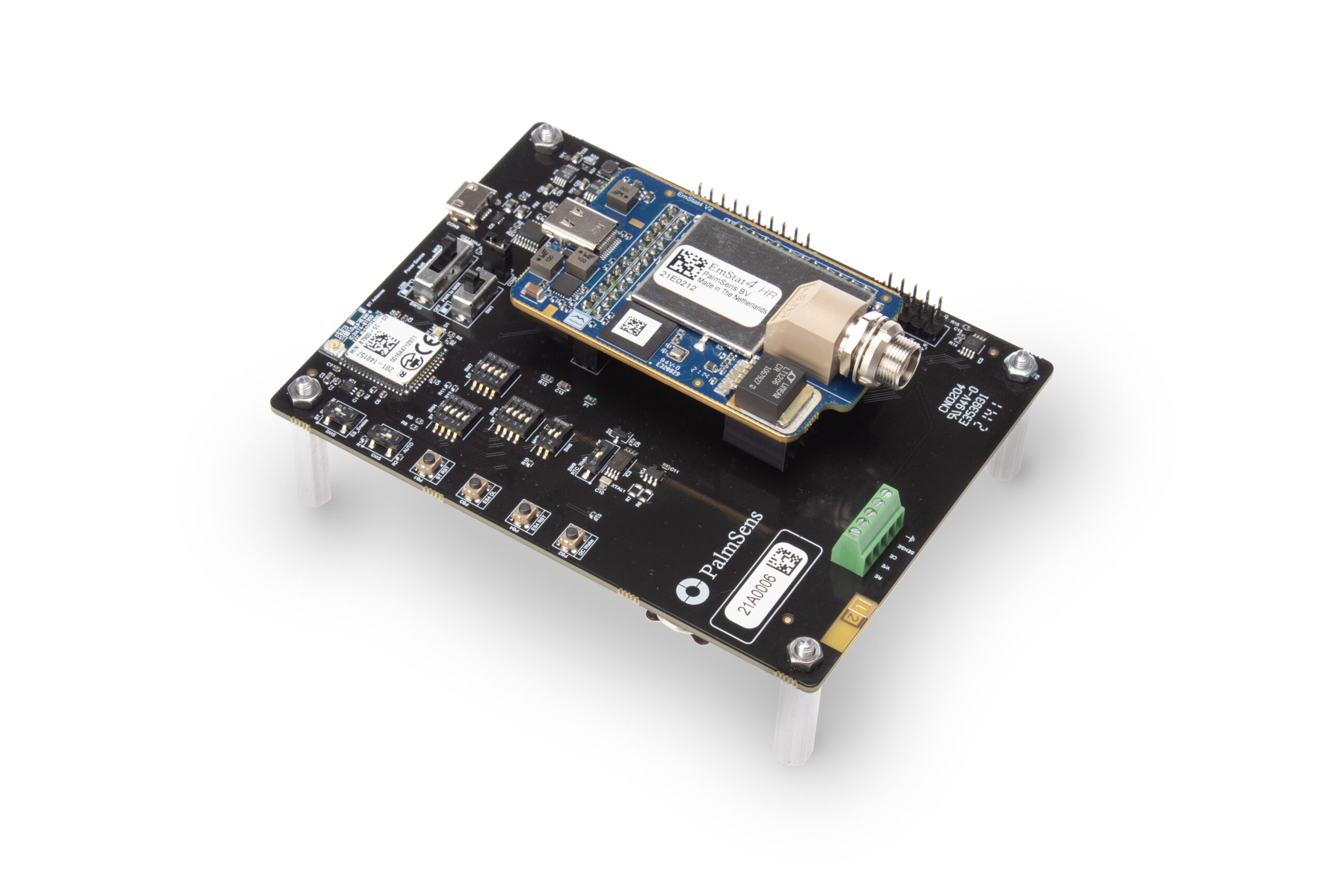
EmStat4M Development Kit
Research grade single-channel potentiostat kit
- Enables rapid prototyping, no programming skills needed
- Run measurements conveniently in PSTrace for Windows
- Develop your own device based on this kit’s schematics
- Many code examples for different languages and platforms
Description
The EmStat4M Development Kit is equipped with a research-grade potentiostat module, which delivers desktop performance. The EmStat4M is a potentiostat/galvanostat supporting Electrochemical Impedance Spectroscopy (EIS). The EmStat4M Development Kit can be used with PSTrace for Windows. You can write your own applications for the EmStat4M Development Kit using our .NET libraries for Windows and Android or using MethodSCRIPT™ and control it from any platform or operating system like an Arduino.
Versions
The EmStat4M Development Kit comes with two different versions of the EmStat4M potentiostat module:
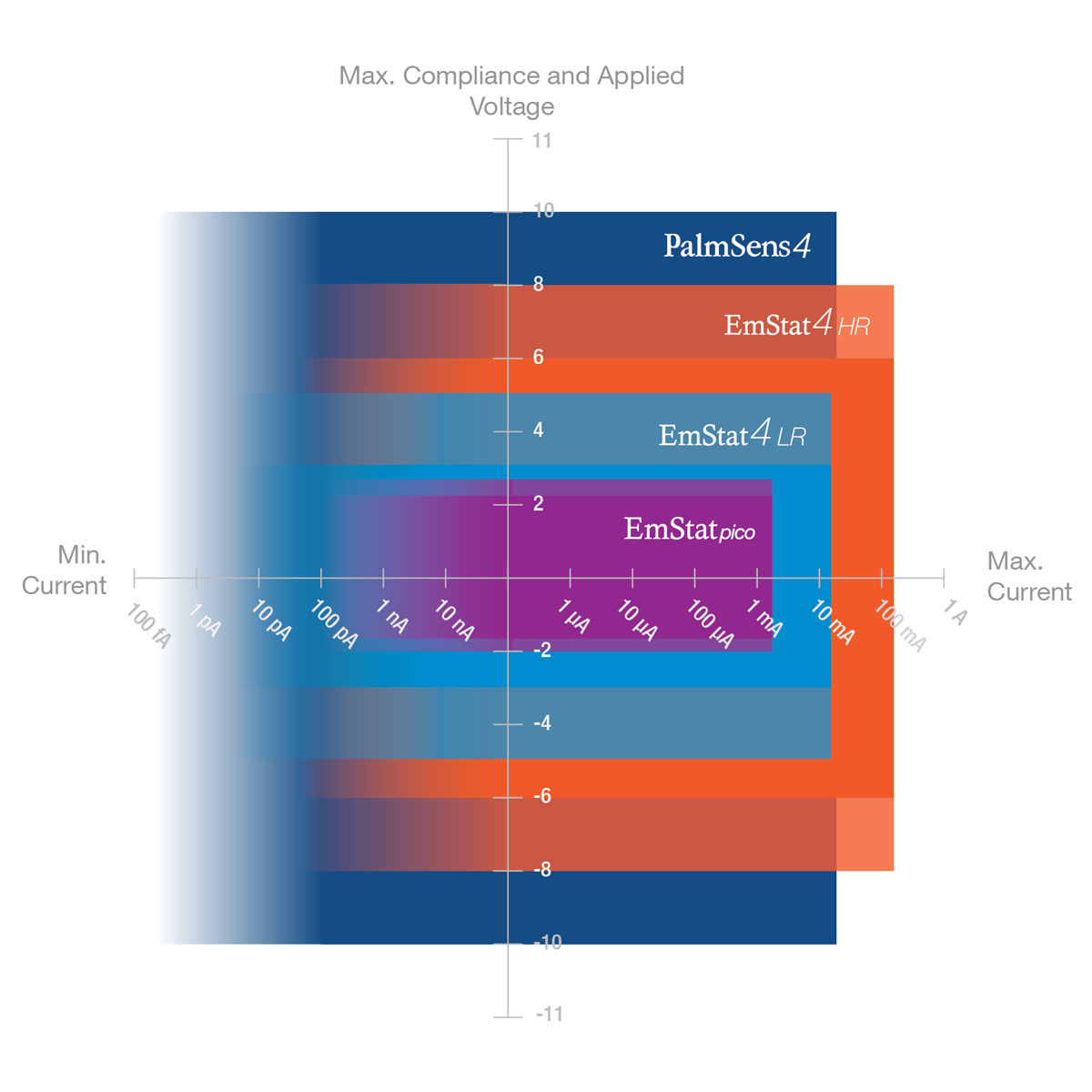
- Low Range (LR): current range from 1 nA to 10 mA, max. 30 mA
- High Range (HR): current ranges from 100 nA to 100 mA, max. 200 mA
See specifications for more information.
Always a backup

Always a backup
The EmStat4M is equipped with 500 MB internal storage memory for storing your measurements and meta data. All internally stored measurements can be browsed and transferred back to the PC easily using the PSTrace software for Windows or with your own software.Included in the EmStat4M Development Kit
The Development kit includes a sensor cable, software, a Development Board (PCBA) and more. The Development Board offers extra peripherals including:
- Wireless communication module (Laird BT900)
- Support for a LiPo battery, incl. charging
- Pin headers for an MKR-series Arduino
- Break-out EmStat4M GPIO pins for easy connection
- Screw-terminals for easy wire connections
- I2C real-time clock (RTC)
- and push buttons for triggering / testing
The EmStat4M module can also be ordered as a bare module or as part of a starter kit:
| Module only | Starter Kit | Development Kit | |
| EmStat4M LR or HR module | |||
| Development Board | – | – | |
| USB-C cable | – | ||
| USB-C splitter cable for extra power (EmStat4M HR only) | – | ||
| Sensor cable (1 meter with 2 mm pins) | – | ||
| 4 or 5 croc clips | – | ||
| Dummy Cell | – | ||
| PSTrace software for Windows (on USB drive) | – | ||
| Quick Start document | – | ||
| Calibration report | – |
Techniques
Voltammetric techniques
Pulsed techniques
Amperometric techniques
Galvanostatic techniques
Electrochemical Impedance Spectroscopy (EIS)
Other
Specifications
| Main specifications of EmStat4M Development Board | |
|---|---|
| Dimensions | 90 x 65 mm |
| Power | USB-C or LiPo battery (battery not included) |
| Main connections | – BT900 Wireless communication module BT v4.0 dual mode (BT and BLE) – Micro-USB (on-board) or USB-C (via module) |
| Cell connections | screw terminals (2.54 mm pitch) and LEMO (EPG.0B.305.HLN) on module |
| Arduino compatibility | Footprint for Arduino MKR series |
| Real Time Clock | On-board IC: S-35390A-T8T1G With CR1225 3V coin cell battery compartment (battery not included) |
| Buttons | 4 buttons for: – EmStat4M Reset – EmStat4M Download – EmStat4M Wake – Wireless communication Module reset |
| DIP switches | DIP switches for: – Power input select – EmStat4M UART select – Wireless communication module UART select – EmStat4M I2C Master select |
The EmStat4M Development Kit is available with two versions of the EmStat4M: LR (Low Range) and HR (High Range). See EmStat4M module for more specifications of the EmStat4M potentiostat module.
| Main differences between the EmStat4M Low and High Range | ||

|

|
|
| EMSTAT4M LR™ | EMSTAT4M HR™ | |
| Potential range | ±3 V | ±6 V |
|---|---|---|
| Max. compliance voltage
The compliance voltage is the maximum voltage that can be applied between the working and counter electrode. Another name could be the maximum cell potential. Continue reading
|
±5 V | ±8 V |
Current ranges
A current range defines the maximum current a potentiostat can measure in a certain range. Continue reading
|
1 nA to 10 mA (8 ranges) | 100 nA to 100 mA (7 ranges) |
| Max. current | ±30 mA | ±200 mA |
| Electrode connections | WE, RE, CE, and ground | WE, RE, CE, Sense, and ground |
Software
PSTrace
PSTrace is designed to be productive immediately after installation, without going through a long learning period. It has three modes; the Scientific mode which allows you to run all the techniques our instruments have to offer, and two dedicated modes for Corrosion analysis and the Analytical Mode. PSTrace is suitable for all levels of user experience.
Features include:
- Direct validation of method parameters
- Automated peak search
- Equivalent Circuit Fitting
- Scripting for running an automated sequence of measurements
- Open data in Origin and Excel with one click of a button
- Load data from the instrument’s internal storage
- and many more…
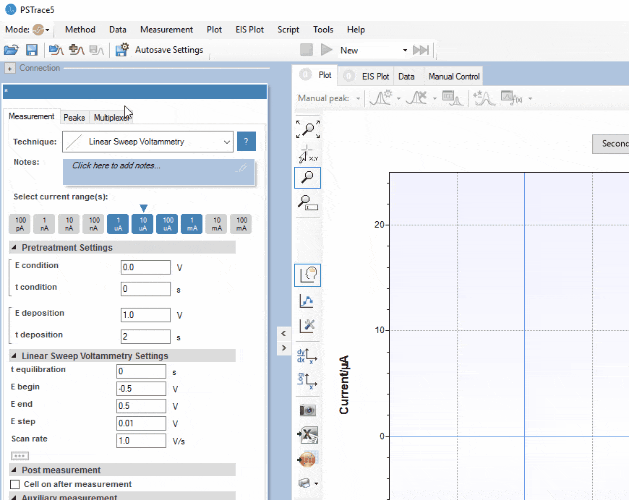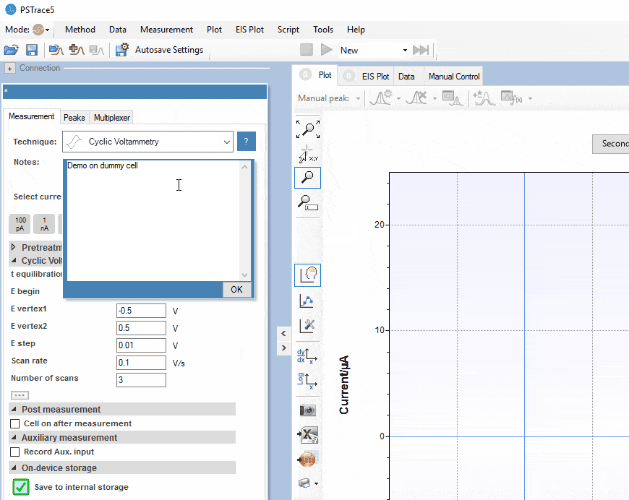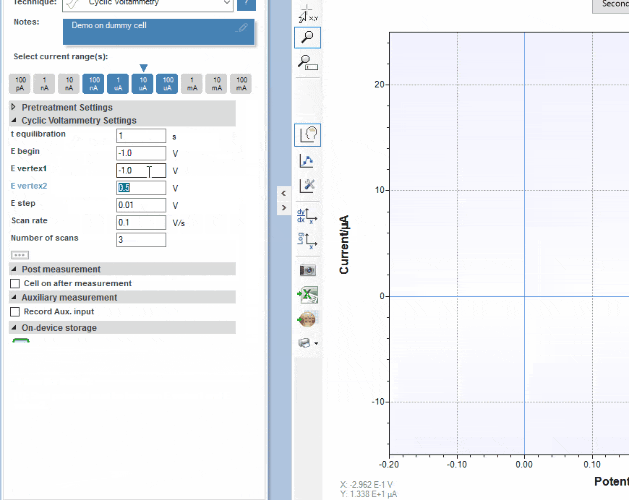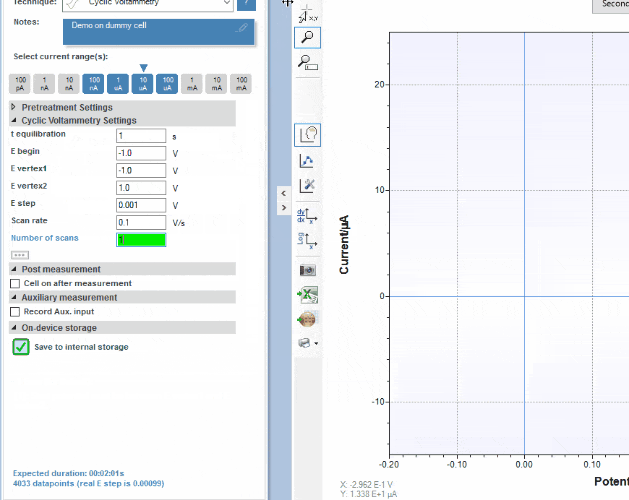
Software Development Kits
PalmSens provides several Software Development Kits (SDKs) to help developers create custom software to control their potentiostat. Each SDK comes with documentation and examples that shows how to use the libraries.
SDKs are available for:
- .NET (WinForms, WPF and Xamarin for Android)
- Python
- LabVIEW
- Matlab

MethodSCRIPT™ Communications Protocol
The Nexus works with MethodSCRIPT™, giving you full control over your potentiostat. The simple script language is parsed on-board, which means no DLLs or other type of code libraries are required. MethodSCRIPT™ allows for running all supported electrochemical techniques, making it easy to combine different measurements and other tasks.
MethodSCRIPT can be generated, edited, and executed in PSTrace.
MethodSCRIPT features includes:
- (Nested) loops and conditional logic support
- User code during a measurement iteration
- Exact timing control
- Simple math operations on variables (add, sub, mul, div)
- Data smoothing and peak detection
- Digital I/O, for example for waiting for an external trigger
- Logging results to internal storage or external SD card
- Reading auxiliary values like pH or temperature
- and many more…

Downloads
Datasheet (1)
| Name | Last updated | |
|---|---|---|
| EmStat4M Datasheet Document with more detailed specifications including module pin-out. | 21-01-26 |
Documentation (13)
| Name | Last updated | |
|---|---|---|
| EmStat4M Communication Protocol V1.4 Describes how to communicate with the EmStat4M directly and how to send MethodSCRIPTS. | 10-10-25 | |
| EmStat4M Development Kit Manual This manual helps you to setup the EmStat4M Development board and explains what is in the Kit. | 25-04-24 | |
| EmStat4M Brochure EmStat4M Brochure including main specifications and practical limitations. | 25-04-24 | |
| MethodSCRIPT v1.5 The MethodSCRIPT scripting language is designed to improve the flexibility of the PalmSens potentiostat and galvanostat devices for OEM users. It allows users to start measurements with arguments that are similar to the arguments in PSTrace. PalmSens provides libraries and examples for handling low level communication and generating scripts for MethodSCRIPT devices such as the EmStat Pico and EmStat4. | 25-03-24 | |
| EmStat4M Communication Protocol V1.3 Describes how to communicate with the EmStat4M directly and how to send MethodSCRIPTS. | 25-03-24 | |
| EmStat Pico and EmStat4 bootloader commands This document explains how to enter the bootloader of the EmStat Pico or the EmStat4M and update the firmware. | 05-10-23 | |
| EmStat4M Communication Protocol V1.2 Describes how to communicate with the EmStat4M directly and how to send MethodSCRIPTS. | 01-02-23 | |
| MethodSCRIPT v1.4 The MethodSCRIPT scripting language is designed to improve the flexibility of the PalmSens potentiostat and galvanostat devices for OEM users. It allows users to start measurements with arguments that are similar to the arguments in PSTrace. PalmSens provides libraries and examples for handling low level communication and generating scripts for MethodSCRIPT devices such as the EmStat Pico and EmStat4. | 01-02-23 | |
| EmStat4M Development Board Connection Card This connection card gives you an overview of the EmStat4M development board connector pin-out and switches. | 14-03-22 | |
| EmStat4M Connection Card This connection card provides an overview of the connector pin-outs. | 14-03-22 | |
| EmStat4M Development Board Schematics The schematics with all pinouts of ports, switches and buttons and a general overview. | 14-03-22 | |
| MethodSCRIPT v1.3 The MethodSCRIPT scripting language is designed to improve the flexibility of the PalmSens potentiostat and galvanostat devices for OEM users. It allows users to start measurements with arguments that are similar to the arguments in PSTrace. PalmSens provides libraries and examples for handling low level communication and generating scripts for MethodSCRIPT devices such as the EmStat Pico and EmStat4. | 19-01-22 | |
| EmStat4M Communication Protocol V1.0 Describes how to communicate with the EmStat4M directly and how to send MethodSCRIPTS. | 14-10-21 |
Other (1)
| Name | Last updated | |
|---|---|---|
| EmStat4M 3D STEP File Contains two STEP files for both EmStat4M LR and HR. Note that the optional USB connector at the bottom is normally not populated. The HR does not include the heat sinks on the heat pads. See also the EmStat4 HR Datasheet. | 19-08-24 |
Software (8)
| Name | Last updated | |
|---|---|---|
| PSTrace PC software for all single channel instruments PSTrace software is shipped as standard with all single channel and multiplexed instruments. The software provides support for all techniques and device functionalities. | 08-07-24 | |
|
MethodSCRIPT code examples
MethodSCRIPT code examples include:
- MethodSCRIPTExample_C - MethodSCRIPTExample_C_Linux - MethodSCRIPTExample_C# - MethodSCRIPTExample_Arduino - MethodSCRIPTExample_Python - MethodSCRIPTExample_iOS - MethodSCRIPTExample_Android Every code example comes with a "Getting Started" document. |
07-07-24 | |
| EmStat4 Firmware v1.3.4 See app note "EmStat Pico firmware updating" for more information about updating built-in and bare EmStat4M modules. | 25-03-24 | |
| EmStat4 Firmware v1.2.3 See app note "EmStat Pico firmware updating" for more information about updating built-in and bare EmStat4M modules. | 08-02-23 | |
| PalmSens SDK for Python PalmSens Python SDK 5.12 with support for instruments from PalmSens BV on Windows systems. | 07-11-22 | |
| Getting started with PalmSens SDK for WPF This manual explains how to use the SDK with the included libraries and examples. | 07-06-21 | |
| Getting started with PalmSens SDK for WinForms This manual explains how to use the SDK with the included libraries and examples. | 07-06-21 | |
| Getting started with PalmSens SDK for Android This manual explains how to use the SDK with the included libraries and examples. | 07-06-21 |
Application Note (1)
| Name | Last updated | |
|---|---|---|
| Migrating to the EmStat4M LR or HR This Application note shows the differences between our older and latest EmStat modules which are relevant when switching your software and electronics design to work with the EmStat4 LR or HR. | 06-10-22 |