Potentiostat
A potentiostat is an electronic device that measures and controls the potential (or voltage) difference between two electrodes.
The measuring electrodes can be very small like micro-electrodes in a conductive solution, but also a coated metal coupon in an acidic environment. A three-electrode setup is also possible.
A potentiostat can be used in the fields of electrochemistry and biochemistry, but also sensor development and battery research.
What is a potentiostat, why use it and how to connect?
In this video we’ll be talking about what a potentiostat, galvanostat and a frequency analyzer are, why you would use them, and how to connect the electrodes.
You can see examples of classic and screen-printed electrodes and four different types of electrochemical techniques.
See all video's on potentiostatsAdvantage of a potentiostat
The word potentiostat comes from potential. In electronics and electrochemistry a potential is stored energy or the “potential to do work”.
Applying a potential with a potentiostat, for instance a PalmSens4, to a conducting surface in a conducting solution can induce a particular electrode current which is measured by the potentiostat while keeping the applied potential constant.
The advantage of a potentiostat is that it has complete control over the applied potential, unlike a normal power source.

What is a potentiostat used for?
A potentiostat is used mainly in electrochemistry. For example, electrochemical researchers want to show how much lead or other heavy metals are present in drinking water (Figure 1), how much iron there is in blood or investigate how rainwater affects the surface of a certain metal (e.g. resulting in corrosion).
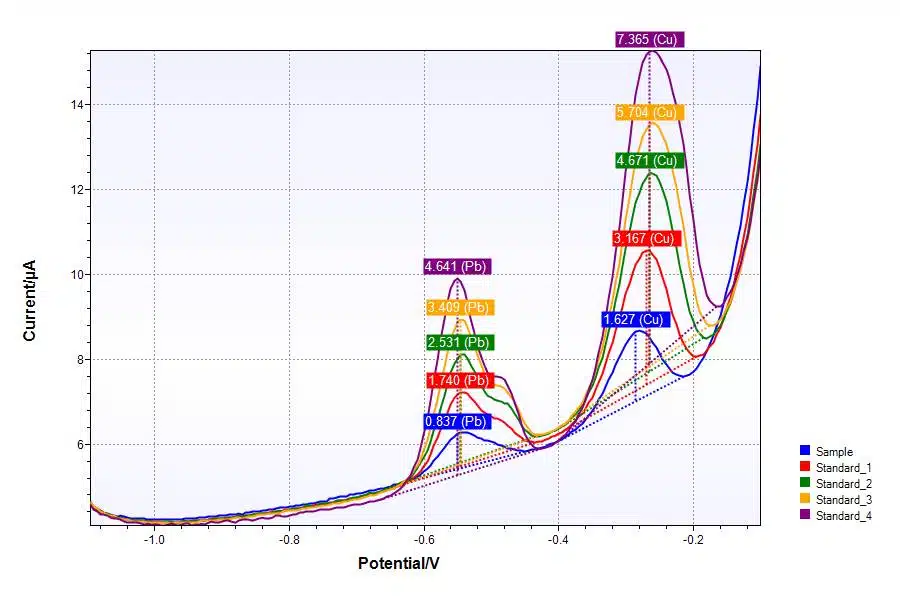
How does a potentiostat work?
A potentiostat applies potential to a certain surface, an electrode. The amount of electrons on the surface is thereby reduced or increased. This causes the liquid to be triggered to deliver or consume electrodes to compensate for this.
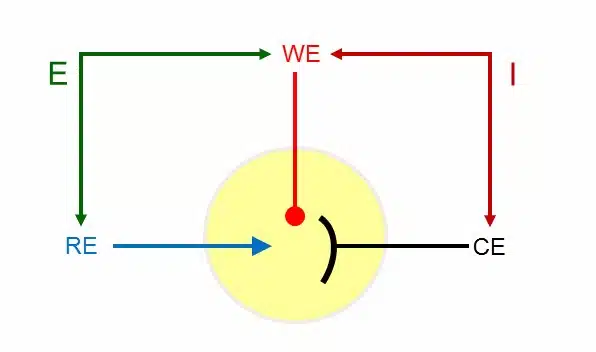
The exchange of electrons per time, the electrode’s current, can be measured by the potentiostat. This is usually done in a three-electrode setup (Figure 2).
Figure 2 | Scheme of a 3-electrode setup for a potentiostat
An electrode made to deliver current of a certain substance is present is called a sensor. This sensor has a certain sensitivity to the substance that you want to measure.
For this reason, there are many different sensors that react in different ways to certain chemical substances.
Sometimes a sensor can be used multiple times, but often they are disposable, so for a one-time use, and the sensor is permanently changed by the reactions happening at the electrodes.
In addition to potentiostats, PalmSens sells sensors of all shapes and sizes for all kinds of measurements.
SensorsDifferent types
There are several types of potentiostats used by electrochemical researchers.
- Most researchers in a university or laboratory use a potentiostat to detect all sorts of possible substances in fluid (for example, the PalmSens4)
- But there are also potentiostats that are only used to detect one particular substance. For this purpose PalmSens makes potentiostat modules, so-called OEM potentiostats.
- PalmSens also provides tailored potentiostats for specific applications like the EmStat Go.


Potentiostat software
Without associated software, there is little to do with your portable potentiostat. PalmSens portable potentiostats are sold including intuitive software, which makes it easy to get started and it can be installed on multiple computers and laptops.
PalmSens also provides an app for Android devices, you can download this free of charge in the Google Play Store.
You can also use all of the currently available spreadsheet software that is useful for creating charts using the Export Data functionality in PSTrace.
About softwarePotentiostat prices
Portable potentiostats usually come at a certain price. However, PalmSens managed to develop a series of portable potentiostats that are highly affordable, definitely with all the given specifications.
E-mail us for a quotation or call us to discuss the possibilities for your research with us.
Request a quotationPotentiostat techniques
Overview of electrochemical techniques that can be performed using a potentiostat.
|
Voltammetric techniques |
Pulsed techniques |
Galvanostatic techniques |
Amperometric techniques |
Potentiostatic/Galvanostatic Impedance spectroscopy (EIS/GEIS) |
Other techniques |
|
Square Wave Voltammetry (SWV) |
|||||
|
|
Open Circuit Potentiometry (OCP) |
||||
Related pages

Portable potentiostat
If you want to carry out your measurements in the field and have results available immediately, you may need a portable battery-powered potentiostat and a USB-powered potentiostat.
Read more
Economical potentiostat
If you want to do electrochemical measurements with a specific purpose in mind, you may need an economically priced potentiostat. PalmSens has several attractively priced instruments for you.
Read more
Multi-channel potentiostat
A multi-channel potentiostat allows you to perform multiple experiments at the same time.
Read more
BiPotentiostat
A BiPotentiostat is a potentiostat with two working electrodes, one counter electrode, and one reference electrode.
Read more
How to choose a potentiostat
The potentiostat’s performance should not limit the results and the software should be user friendly and easy to use.
Read moreDefinition of a potentiostat
- Potentiostat
- An electronic device that measures and controls the potential (or voltage) difference between two electrodes is called a potentiostat. The advantage of a potentiostat is that it has complete control over the applied potential, unlike other power sources, while measuring the response current.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is a potentiostat?
The word potentiostat comes from potential. In electronics and electrochemistry a potential is stored energy or the “potential to do work”.
Applying a potential with a potentiostat, for instance a PalmSens4, to a conducting surface in a conducting solution can induce a particular electrode current which is measured by the potentiostat while keeping the applied potential constant.
The advantage of a potentiostat is that it has complete control over the applied potential, unlike a normal power source.
Which potentiostat do I need?
An electrochemist typically spends many months together with a potentiostat to get research done. The potentiostat’s performance should not limit the results and the software should be user friendly and easy to use. Here are six factors to consider before buying a potentiostat. Read more
What is a potentiostat used for?
A potentiostat is used mainly in electrochemistry. For example, electrochemical researchers want to show how much lead or other heavy metals are present in drinking water, how much iron there is in blood or investigate how rainwater affects the surface of a certain metal (e.g. resulting in corrosion). Read more…
How does a potentiostat work?
A potentiostat applies potential to a certain surface, an electrode. The amount of electrons on the surface is thereby reduced or increased. This causes the liquid to be triggered to deliver or consume electrodes to compensate for this. The exchange of electrons per time, the electrode’s current, can be measured by the potentiostat. This is usually done in a three-electrode setup (Figure 2).
An electrode made to deliver current of a certain substance is present is called a sensor. This sensor has a certain sensitivity to the substance that you want to measure. For this reason, there are many different sensors that react in different ways to certain chemical substances.
Sometimes a sensor can be used multiple times, but often they are disposable, so for a one-time use, and the sensor is permanently changed by the reactions happening at the electrodes.
What are the different types of potentiostats and their applications?
Electrochemistry is a broad field with many different applications. This is reflected in the electrochemical instruments as well. Potentiostats, Galvanostats, and Impedance Analyzers are rather versatile but often have a focus on certain properties added with an application in mind.
Many researcher instruments are actually a combination of potentiostats, galavanostats, and impedance analyzers. Often people will call these combinations just potentiostats and not potentiostat/galvanostat.
What is the difference between a potentiostat and a galvanostat?
A potentiostat controls the potential and measures the resulting current. A galvanostat controls the current and measures the resulting potential. Most modern instruments are combinations of potentiostats and galvanostats.
What are the key specifications and parameters of a potentiostat?
Devices that are as complex as a potentiostat have many different specifications and parameters listed in their documentation.
The first parameters to look at are the potential range and the current range. The currents and voltages, you want to apply and measure, must be within the capabilities of the instrument.
How does a potentiostat control the potential and current of an electrochemical cell?
A short introduction video to potentiostats is available in our knowledge base. A very simplified description is that a potentiostat keeps the potential between two electrodes, the working electrode and the reference electrode, at a set potential.
Current will flow between the working electrode and a third electrode, the counter electrode. This way the reference electrode has a constant electrochemical potential and can be used by the potentiostat as a fixed reference point.
What are the benefits of using a potentiostat in electrochemical experiments?
An impedance analyzer applies a sine wave-shaped potential profile to the cell and calculates from the sine wave current response the impedance and phase shift of the cell.
This makes potentiostats more versatile and their active control of a parameter more powerful than regular meters.
There are also specialized potentiostats on the market, that are labeled according to their application, e.g. battery cyclers. So, you might have used a potentiostat without knowing.
How does a potentiostat measure electrochemical impedance and cyclic voltammetry?
Electrochemical Impedance Spectroscopy (EIS) and Cyclic Voltammetry (CV) are very popular electrochemical techniques and both of them have been covered in separate articles in our knowledge base:
What are the key factors to consider when choosing a potentiostat for a specific application?
- We recommend first considering the technical specifications that are available in the documentation of an instruments, which are covered in this FAQ.
- The next important point for most customers is the software. The software should support the technique you require.
- Besides the specifications of the electrochemical measurements there are more technical features that could be interesting for your application.
- Other factors concern the purchasing process. Important factors are transparent price information, support, how difficult it is to set up the device, and how long the guarantee is.
What are some common techniques and methods used with potentiostats in electrochemistry?
There are many different techniques and methods in electrochemistry. The differences between the techniques are the profile of the applied potential or current and when the signal is measured.
Techniques can be classified by what is controlled, for example, potentiostatic techniques, when the potential is controlled, and galvanostatic techniques, when the current is controlled.
How can a potentiostat be used to study battery performance and degradation?
Batteries are systems that store electrical energy as chemical energy. A charged battery has two parts that have different potentials, which can be used to apply that potential to other devices. A current will flow, and the connected device is powered.
Electrochemical measurements can characterize batteries, for example how often they can be charged and discharged, how much charge is stored in the battery, or how the battery changes over time.
There are multiple methods for characterizing batteries, which one is applied usually depends on what parameter needs to be observed. The most common techniques are Electrochemical Impedance Spectroscopy (EIS) and Charge-Discharge curves.